Figure 2.
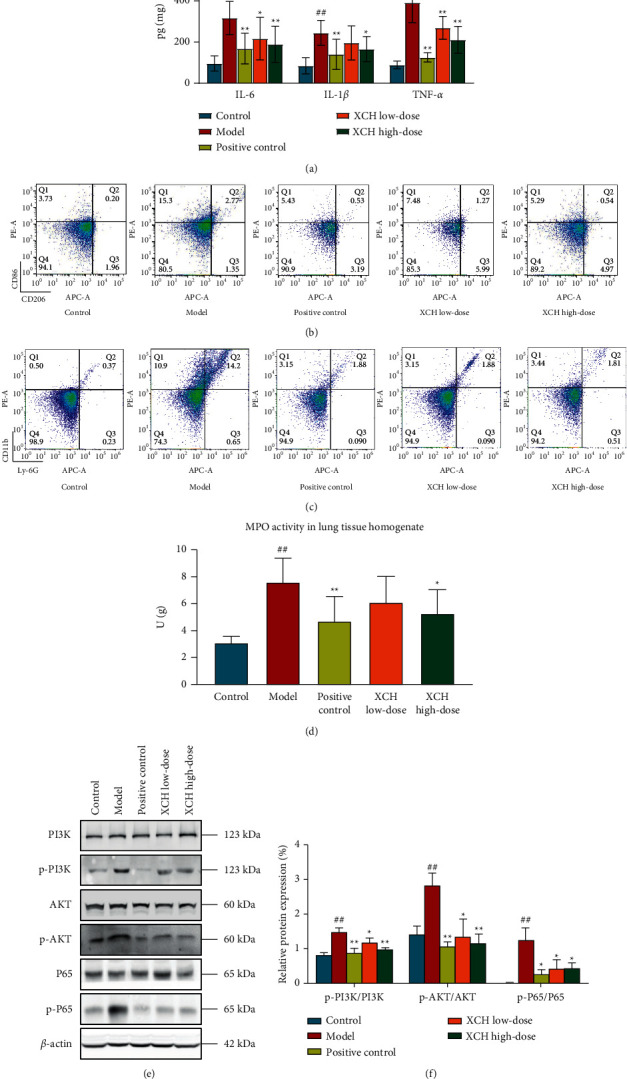
XCH reduced the inflammatory response in viral pneumonia model mice induced by poly (I:C). (a) XCH treatment decreased the levels of proinflammatory cytokines in BALF. (b) Flow cytometry showed that XCH treatment decreased the ratio between CD86+ and CD206+ cells in BALF. (c) Flow cytometry showed that XCH treatment decreased the proportion of Ly6G+CD11b+ cells in BALF. (d) XCH treatment decreased the activity of MPO in lung tissue homogenate. ((e) and (f)) Western blot showed that XCH treatment inhibited the activation of PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway. Control, model, positive control, XCH low-dose, and XCH high-dose groups (n = 10 per group). ##: p < 0.01 compared with the control group; ∗: p < 0.05 compared with the model group; ∗∗: p < 0.01 compared with the model group.
