Fig. 1.
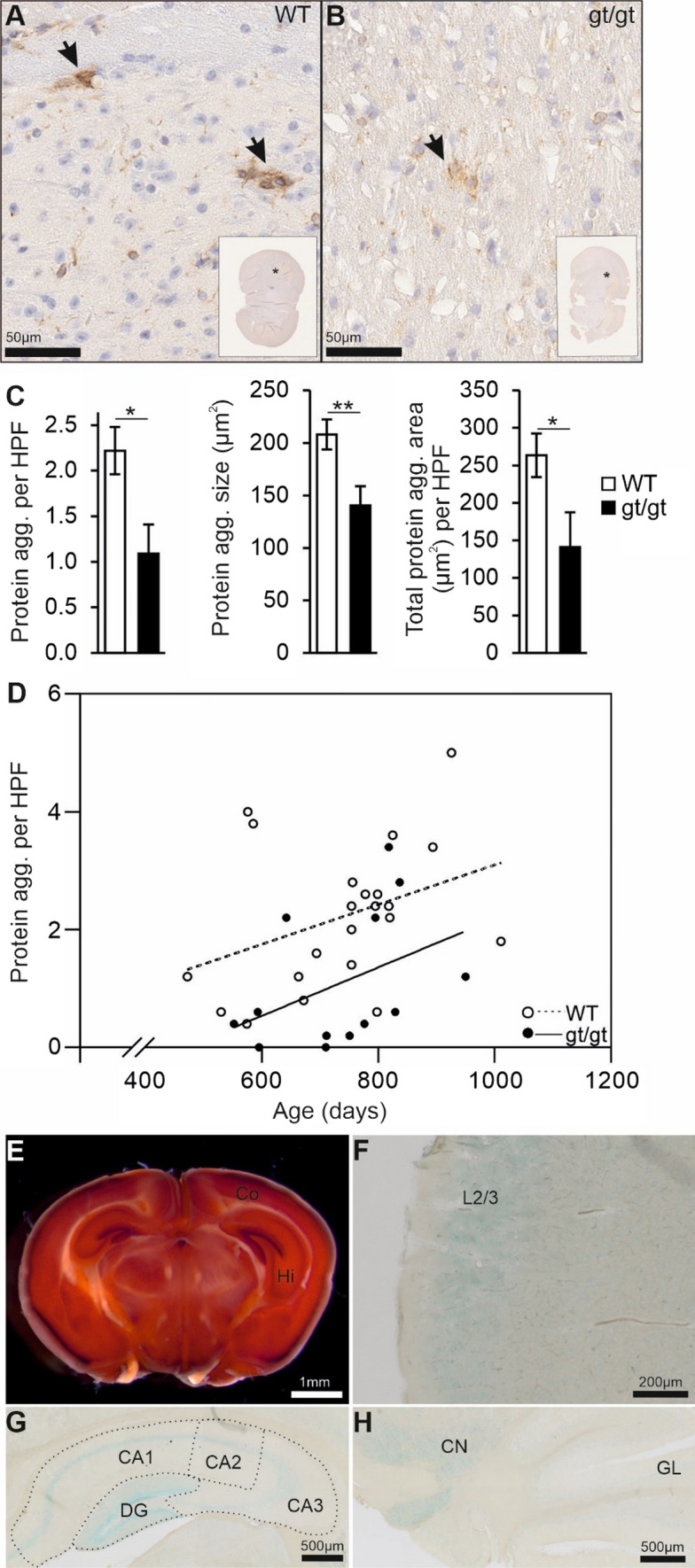
HIF-P4H-2 deficient mice display less protein aggregates in the brain in senescence. A, B Aged-matched Aβ-stained senescent wild-type (WT) and Hif-p4h-2gt/gt (gt/gt) brain tissue. Scale bars = 50 µm. The brain regions of the enlarged pictures are shown in the inset by an asterisk. Arrows indicate the Aβ-positive protein aggregates. C Number of Aβ-positive protein aggregates, the average size of individual aggregates and the total aggregate-covered area per HPF. Five HPF/mouse were analyzed. D Correlation of the number of Aβ-positive protein aggregates with age. E X-gal-stained coronal gt/gt brain section. Scale bar = 1 mm. F X-gal-stained cross-section of the auditory cortex in a gt/gt mouse. The positivity is largely limited to layer 2/3. Scale bar = 200 µm. G, H X-gal-stained coronal gt/gt hippocampus and coronal cerebellum, respectively. Scale bars = 500 µm. Data are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 in T-test. In C and D, n = 22 WT, 13 gt/gt males. agg. Aggregate, CA cornu ammonis, CN cerebellar nuclei, Co cortex, DG dentate gyrus, GL granular layer, Hi hippocampus, HPF high-powered field, L2/3 layer 2/3
