Fig. 4. Pathogen suppression capability of predatory protists and their potential interactions with Bacillus and NRPS gene.
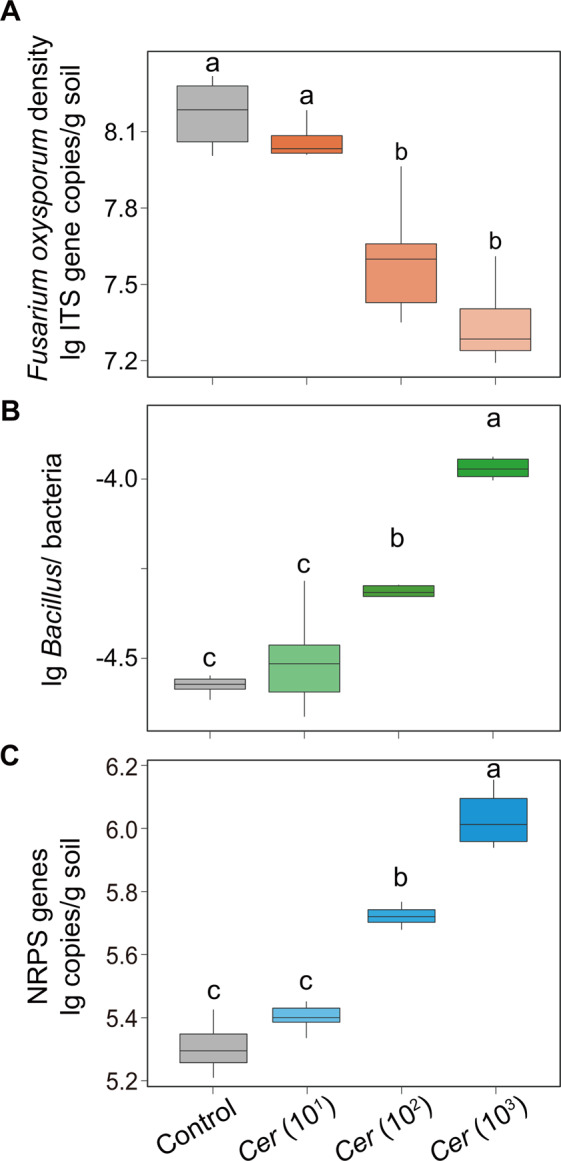
A The effects of different concentrations of predatory protists on Fusarium oxysporum density. B The effects of different concentrations of predatory protists on the ratio of Bacillus density to total bacteria density. C The effects of different concentrations of predatory protists on the abundance of nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) gene. In panels A–C, bars with different letters indicate significant differences as defined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s HSD test (p < 0.05). In the control, no protists were added. Cer (101): Cercomonas lenta strain ECO-P-01 (1.0 × 101 cells g−1 dry soil); Cer (102): Cercomonas lenta strain ECO-P-01 (1.0 × 102 cells g−1 dry soil); Cer (103): Cercomonas lenta strain ECO-P-01 (1.0 × 103 cells g−1 dry soil). Bacillus/ bacteria = the ratio of Bacillus density to total bacteria density.
