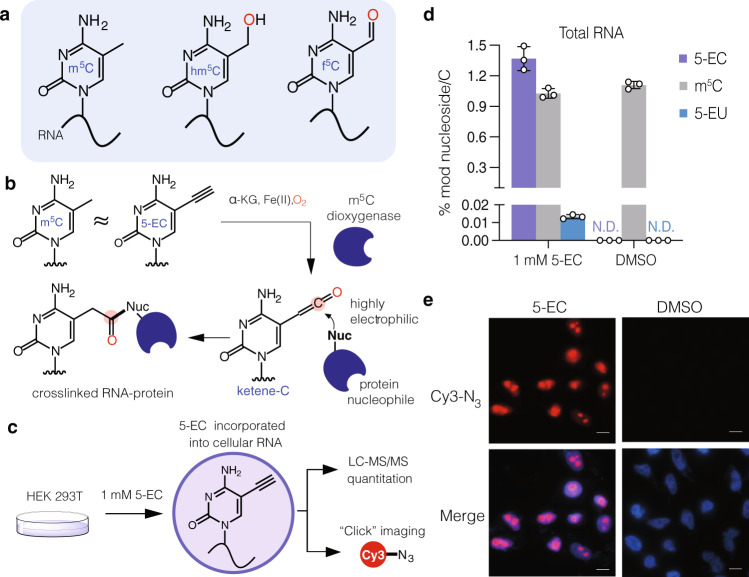
Fig. 1. Probing m5C oxidation in RNA with 5-ethynylcytidine (5-EC).
a Structure of reported m5C oxidation products in RNA. b Proposed capture of m5C dioxygenases by metabolic labeling with 5-EC. 5-EC mimics m5C in RNA and upon enzymatic oxidation generates an electrophilic ketene that can covalently trap nearby nucleophiles. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. c Strategy for metabolic labeling with 5-EC. The nucleoside is fed to mammalian cells and incorporated into cellular RNA. Incorporation can be measured by quantitative mass spectrometry or click chemistry imaging. d LC-MS/MS analysis of 5-EC, m5C, and 5-EU in total RNA of HEK293T cells after treatment with 1 mM 5-EC or DMSO for 16 h. Three independent biological replicates were analyzed. Data represent mean values ± s.d. e Fluorescence microscopy analysis of 5-EC cellular incorporation. HEK293T were treated with 1 mM 5-EC or DMSO for 16 h, fixed and labeled with Cy3-N3 before imaging by fluorescence microscopy. The experiments were repeated three times independently with similar results. Scale bar = 10 µM.