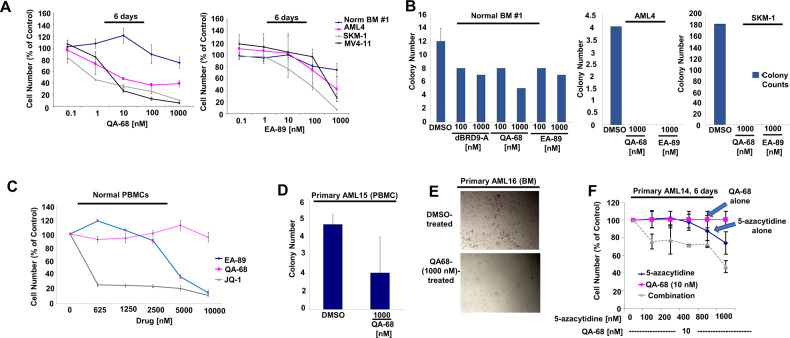
Fig. 5. Targeted loss of BRD9 protein by degradation leads to inhibition of primary AML and ALL cell growth and colony formation.
A Proliferation assays: Normal bone marrow cells (sample #1) and primary AML4 cells (secondary AML) treated with QA-68 and EA-89. 6-day assay. SKM-1 and MV4-11 cell lines were tested as positive controls (B) QA-68, EA-89 and dBRD9-A effects on normal bone marrow or primary AML4 colony formation using MethoCult H4434 Classic methylcellulose medium (with cytokines) and IMDM culture media. SKM-1 cells were tested as a positive control. Shown are colony counts taken following 8 days from the start of the assay. C Treatment of normal PBMCs with QA-68 or EA-89 versus the BRD4 inhibitor, JQ1. 4-day assay. D Effects of QA-68 treatment on primary AML PBMCs (sample AML15) colony formation, using MethoCult Enriched H4435 methylcellulose medium and IMDM culture media. Shown are colony counts taken following 12 days from the start of the assay. E Effects of QA-68 treatment on primary AML patient BM cells (sample AML16) colony formation, using MethoCult Enriched H4435 methylcellulose medium and IMDM culture media supplemented with cytokine cocktail and FLT3L. Shown are representative images from a well following 6 days from the start of the assay. F Treatment of primary AML cells (sample AML14) with QA-68 alone, 5-azacytidine alone, or a combination. 6-day assay.