Figure 4.
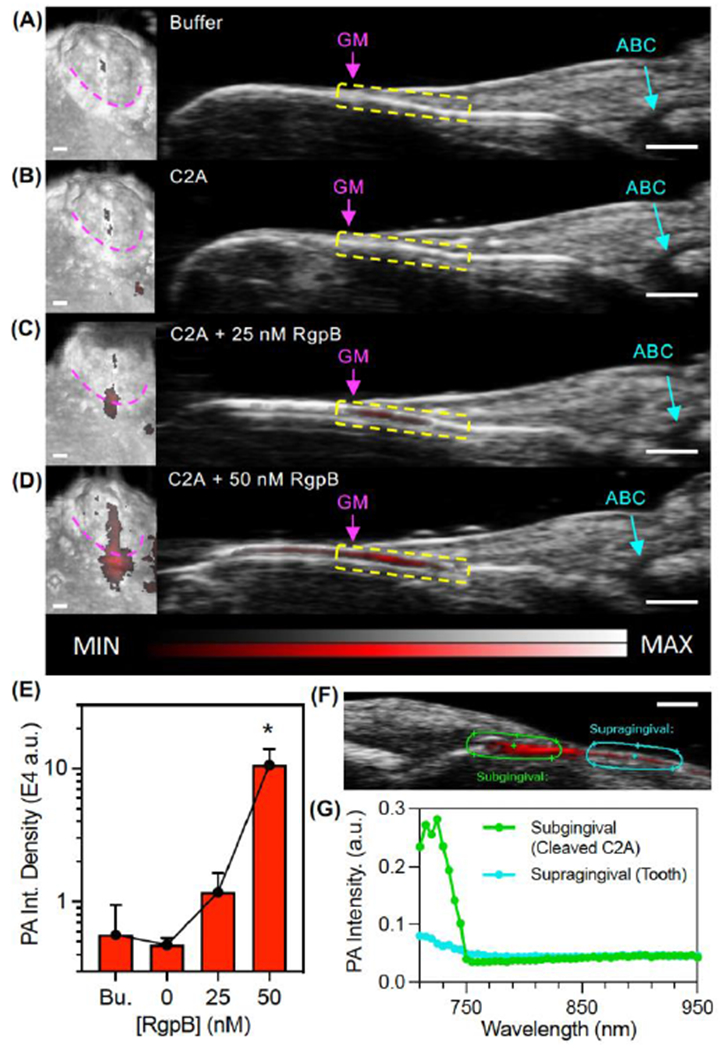
Photoacoustic-ultrasound imaging of RgpB-activated C2A probe in the gingival sulci of porcine jaws. (A) Left: 3D rendering of a mandibular second molar with PA signal (red) overlay on the US image (grayscale) following administration of Tris buffer at the gingival margin (pink). Right: cross-sectional image of the midsagittal plane of the tooth with the gingival margin (GM), alveolar bone crest (ABC), and gingival sulcus (yellow) labeled. (B-D) Images of the same site following administration of (B) C2A alone, (C) C2A + 25 nM RgpB, and (D) C2A + 50 nM RgpB. The sulcus was irrigated with water between imaging events. (E) Quantitation of the PA signal via integrated density for the maximum intensity projection of each PA image (n = 3 mandibles). (F) PA-US spectral image of subgingival signal corresponding to injected C2A (green ROI) and supragingival signal corresponding to background from the tooth surface (teal). (G) PA spectra of the regions in Panel F. Scale bars = 1 mm.
