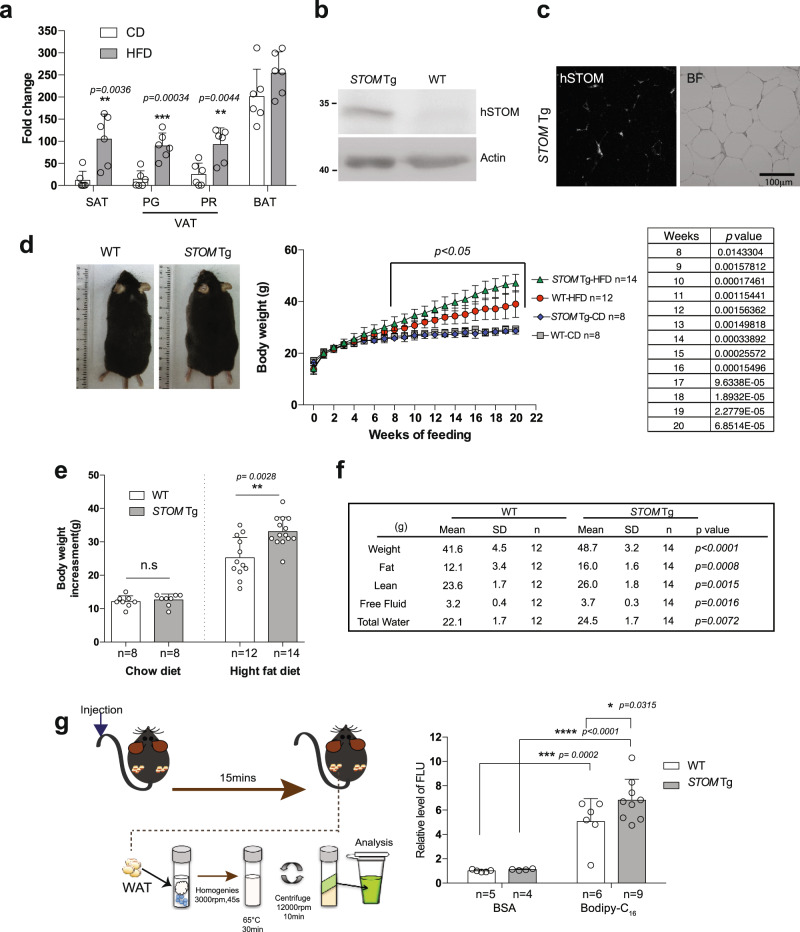
Fig. 4. Stomatin transgenic mice fed with high-fat diet were more obese than the control mice.
a Real-time qPCR analyses validated increased stomatin gene expressions in SAT, VAT, including Perigonadal fat pad (PG) and Perirenal fat pad (PR), and BAT after regular CD or HFD feeding. Mean ± s.d. for six mice. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001, by multiple unpaired t test. b Western blotting revealed high expressions of human stomatin (hSTOM) proteins in stomatin transgenic mice (STOM Tg). c The exogenous hSTOM proteins were present mainly on the plasma membranes of adipocytes in fat tissues of STOM Tg mice. d Body weight changes of STOM Tg and wild type (WT) mice during CD or HFD feeding for 20 weeks. Mean ± s.d. of mice, *P < 0.05 analyzed by multiple unpaired t tests. Representative photos of the mice are shown. e Body weight increments after 20-week feeding were measured. Each dot represents one mouse. While no difference was noticed in animals fed with CD, body weight gains were significantly higher in HFD-fed STOM Tg, compared to HFD-fed WT mice. Mean ± s.d. is shown. n.s = non-significant. **P < 0.01 by two-sided unpaired t-test. f The mass of whole body, fat, lean, free fluid, and total water were calculated by body composition analyzer for HFD-fed STOM Tg and HFD-fed WT mice. P values were examined by multiple unpaired t test. g Fatty acid uptake was measured in vivo. Fluorescently-labeled fatty acid Bodipy-FL-C16, or BSA, were injected into tail vein of STOM Tg or WT mice. After 15 min, lipid portions of white adipose tissue (WAT) from the animal were extracted and their fluorescence signals that represented lipid uptake were quantified. Data shown are fold changes of fluorescence intensity using BSA injected to WT mice as the reference. Each dot represents one mouse. Mean ± s.d. for mice from two independent experiments. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by two-way ANOVA. Source data are provided as a Source data file.