Figure 1. scRNAseq of AmbCardiac neurons identifies a genetic signature of brainstem parasympathetic neurons.
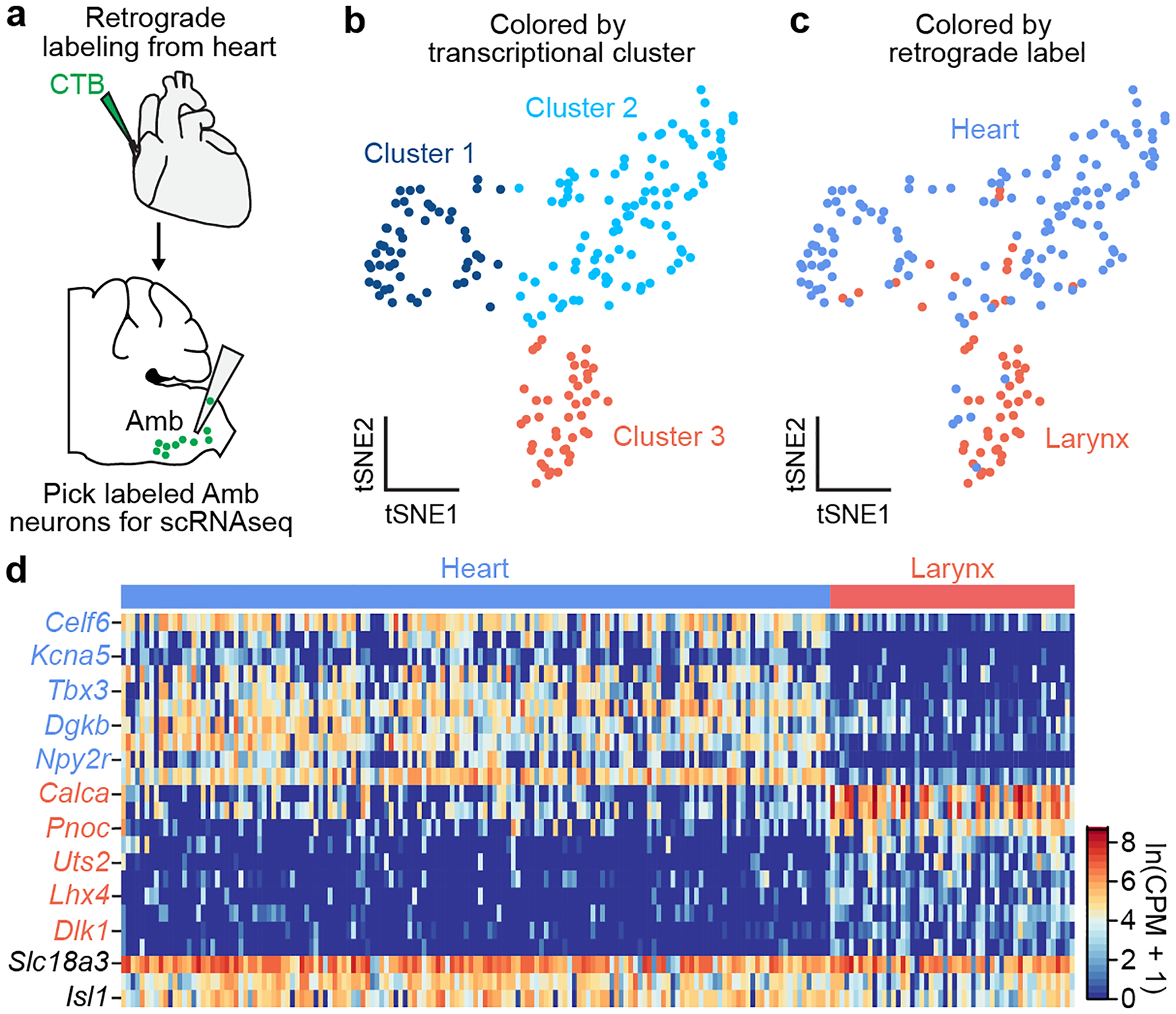
a, Strategy for isolating AmbCardiac neurons. Fluorescent CTB was injected into the pericardial space, and 1–3 days later the retrograde-labeled cardiac-innervating neurons in the nucleus ambiguus (AmbCardiac neurons) were aspirated from acute physiological brainstem slices, then processed for scRNAseq. In separate mice (not shown), CTB was injected into the cricothyroid laryngeal muscle to similarly visualize, aspirate, and process control AmbLaryngeal neurons. b, t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding (tSNE) plot comparing Amb neuron scRNA-seq expression profiles (dots). Note three transcriptionally distinct neuronal clusters defined by nearest neighbor analysis. c, tSNE plot of same Amb neurons as (b) but colored by their retrograde label origin. AmbLaryngeal neurons largely comprise cluster 3, whereas AmbCardiac neurons were largely split between clusters 1 and 2. d, Heat map showing log-transformed expression levels of selected genes differentially expressed between AmbCardiac and AmbLaryngeal neurons. Names in black, expected pan-Amb genes. Mouse brain image and those in Figs. 3, 4, 6, 7 and Extended Data Figs. 5 and 7 are reproduced from the Paxinos and Franklin atlas35.
