Extended Data Figure 5. Viral targeting of ACP or ACV neurons.
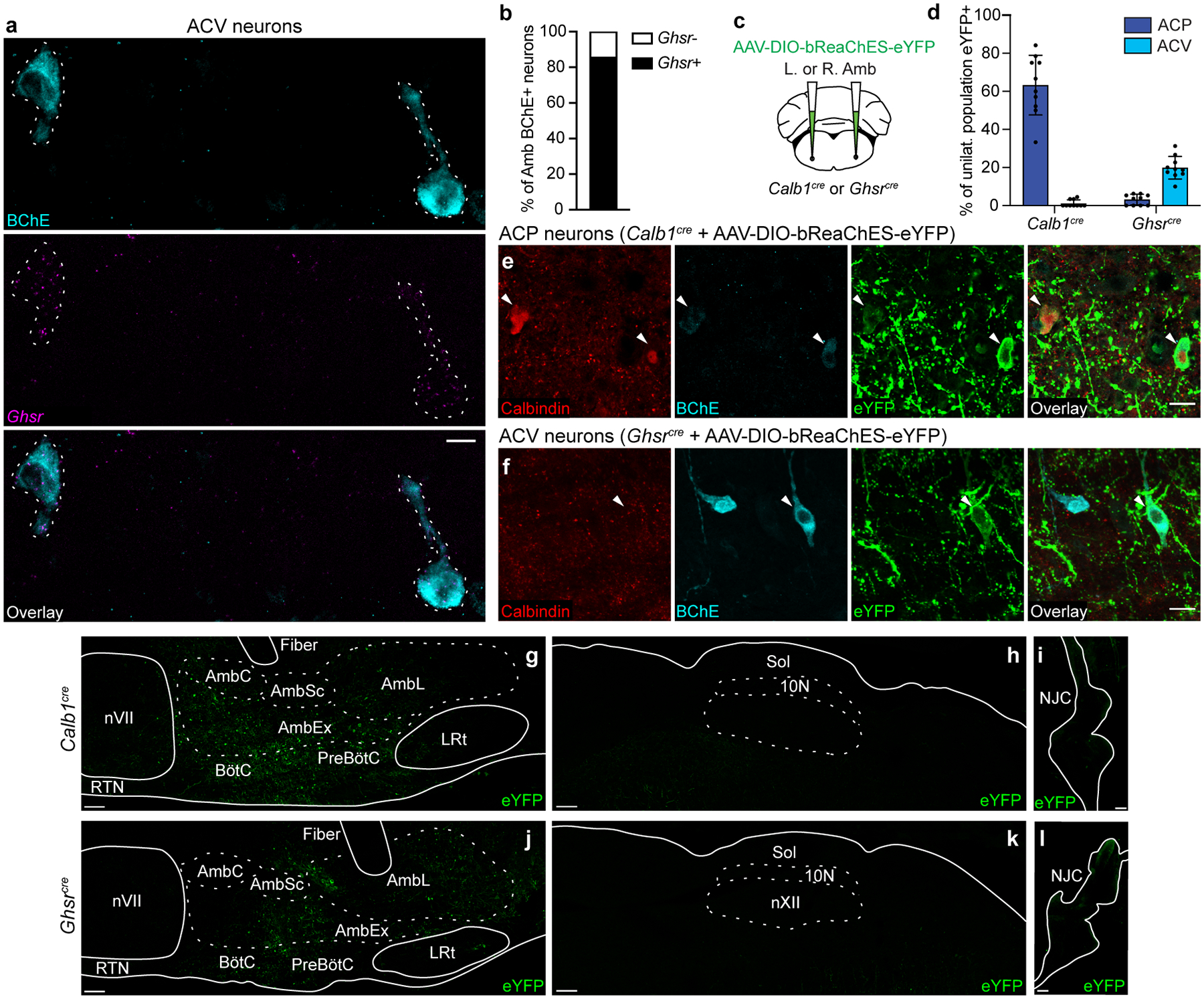
a, Combined immunostaining and smFISH showing overlap between BChE protein expression (cyan) and Ghsr mRNA expression (purple) in ACV neurons (dashed outlines). Bar, 100 μm. b, Quantification of panel a showing fraction of BChE+ ACV neurons that express Ghsr in Amb (n = 3 mice, 21 neurons total). c, Strategy for targeting ACP or ACV neurons. A Cre-dependent AAV encoding the opsin bReaChES fused to eYFP was delivered to the left or right Amb in Calb1cre mice (to target ACP neurons) or Ghsrcre mice (to target ACV neurons). d, Targeting specificity of AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP vector used for left- and right-sided terminal mapping and optogenetics experiments in Figs. 3–4 (n = 10 Calb1cre, n = 10 Ghsrcre mice, n = 612 neurons total, mean ± s.d.). eYFP expression on the correct side of the brainstem was verified for all mice, and % of population eYFP+ was calculated for the unilateral (injected) Amb. When injected into Calb1Cre mice, ACP (calbindin+) neurons were specifically labeled. When injected into Ghsrcre mice, ACV (BChE+) neurons were specifically labeled, though note lower efficiency than the ACP neuron strategy. e, Immunostaining of Rostral Amb ACP neurons in Calb1cre mice injected with AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP vector. Two calbindin+ neurons were eYFP-positive (arrowheads), indicating bReaChES-eYFP expression. f, Immunostaining of caudal Amb ACV neurons in Ghsrcre mice injected with AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP vector. A BChE+ neuron was eYFP-positive (arrowhead), indicating bReaChES-eYFP expression. Bars, 20 μm. g, Distribution of eYFP expression after rostral Amb injection of AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP in a Calb1cre mouse. Note eYFP expression in the Amb external formation (AmbEx) and in overlapping Bötzinger complex (BötC) and pre-Bötzinger complex (preBötC) breathing control regions, with sparing of Amb compact formation (AmbC, esophageal motor neurons), Amb semicompact formation (AmbSc, pharyngeal motor neurons), Amb loose formation (AmbL, laryngeal motor neurons), facial motor nucleus (nVII), retrotrapezoid nucleus (RTN), and lateral reticular nucleus (LRt). Bar, 100um. h, Sagittal brainstem section showing lack of eYFP expression in dorsal motor nucleus of vagus (10N) and nucleus of the solitary tract (Sol) after AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP injection into Amb in Calb1cre mouse. Bar, 100um. i, Whole-mount immunostaining showing minimal eYFP expression in the nodose-jugular complex (NJC) after AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP injection into Amb in Calb1cre mouse. Bar, 100 μm. j, Distribution of eYFP expression after caudal Amb injection of AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP in a Ghsrcre mouse. Note eYFP expression in AmbEx, AmbL, and in overlapping BötC and preBötC, similar to Calb1cre mice in panel g but with a more caudal distribution. Bar, 100um. k, Sagittal brainstem section showing lack of eYFP expression in 10N and Sol after AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP injection into Amb in Ghsrcre mouse. Bar, 100um. l, Whole-mount immunostaining showing lack of eYFP expression in the NJC after AAV-DIO-bReaChES-eYFP injection into Amb in Ghsrcre mouse. Bar, 100 μm.
