Extended Data Figure 6. Cardiac GP projection targets of ACP and ACV neurons.
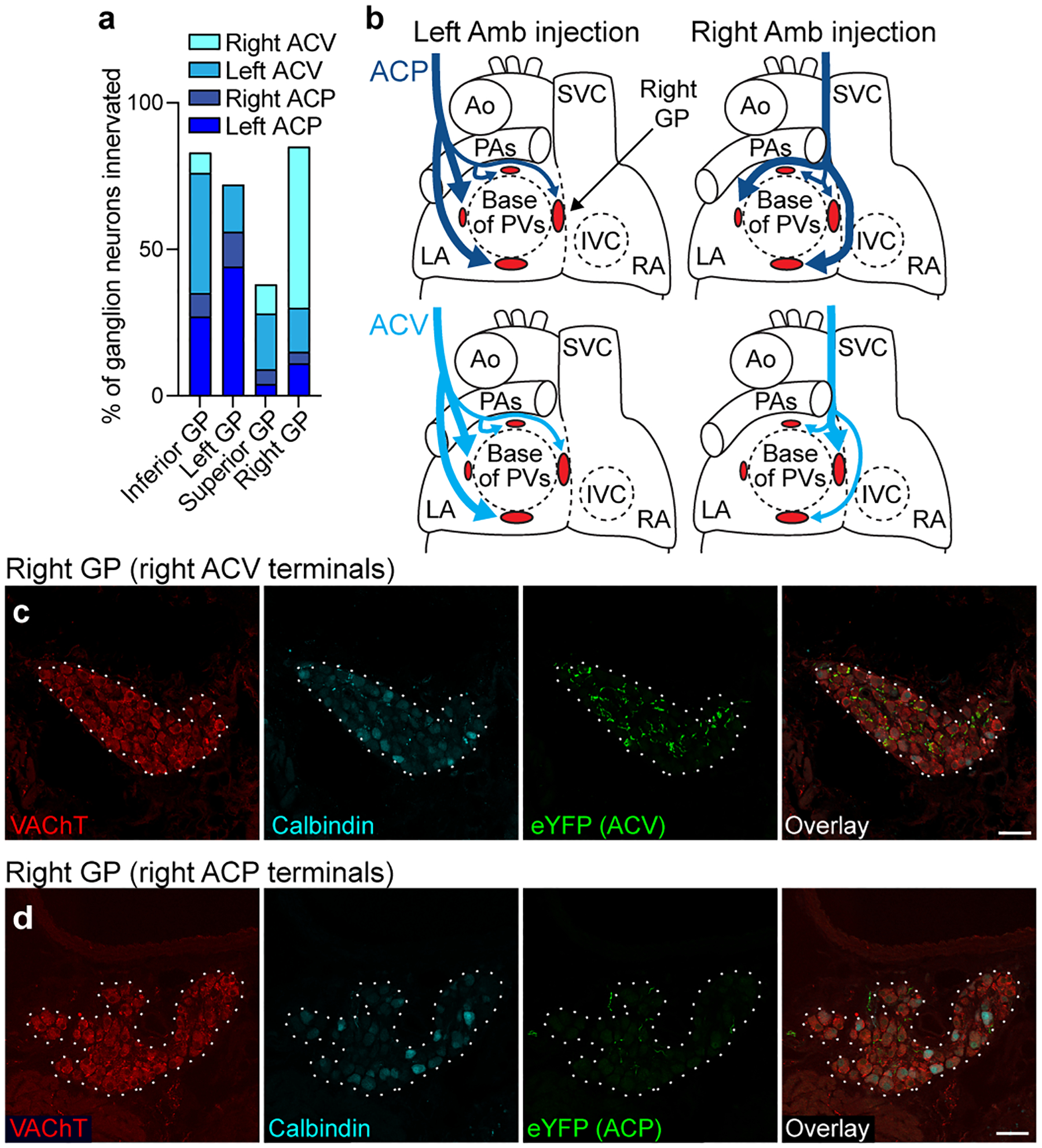
a, Estimated proportions of ganglion neurons within each indicated ganglionated plexus (GP) that receive innervation from a given side and cell type, labeled as in Fig. 3 (n = 2067 neurons total, 2 mice per unilateral cell type). Remaining cells not innervated by ACP or ACV neurons are likely innervated by dorsal motor nucleus of vagus or possibly other ganglion neurons. b, Schematics (based on a) of left and right atria (LA and RA) of heart showing innervation of four cardiac GPs (red ovals) by left and right ACP (dark blue) and ACV (light blue) neurons. Thick arrows, dense innervation; thin arrows, sparse innervation. Note left and right ACP neurons innervate same set of GPs, whereas left and right ACV neurons innervated different sets of GPs. Ao, aorta; PA, pulmonary artery; PVs, pulmonary veins; SVC, superior vena cava; IVC, inferior vena cava. c, Immunostaining of the right cardiac GP (dotted outline) after right ACV fibers were labeled with eYFP. The right GP stained positive for vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT), and many eYFP+ ACV fibers innervate ganglion neurons within the GP. d, Immunostaining of the right GP (dotted outline) after right ACP fibers were labeled with eYFP as in Fig. 3. In contrast to right ACV fibers, few eYFP+ fibers from right ACP neurons were found innervating right GP ganglion neurons. Bars, 50 μm.
