Extended Data Figure 8. c-Fos negative control studies and heart rate response to dive reflex.
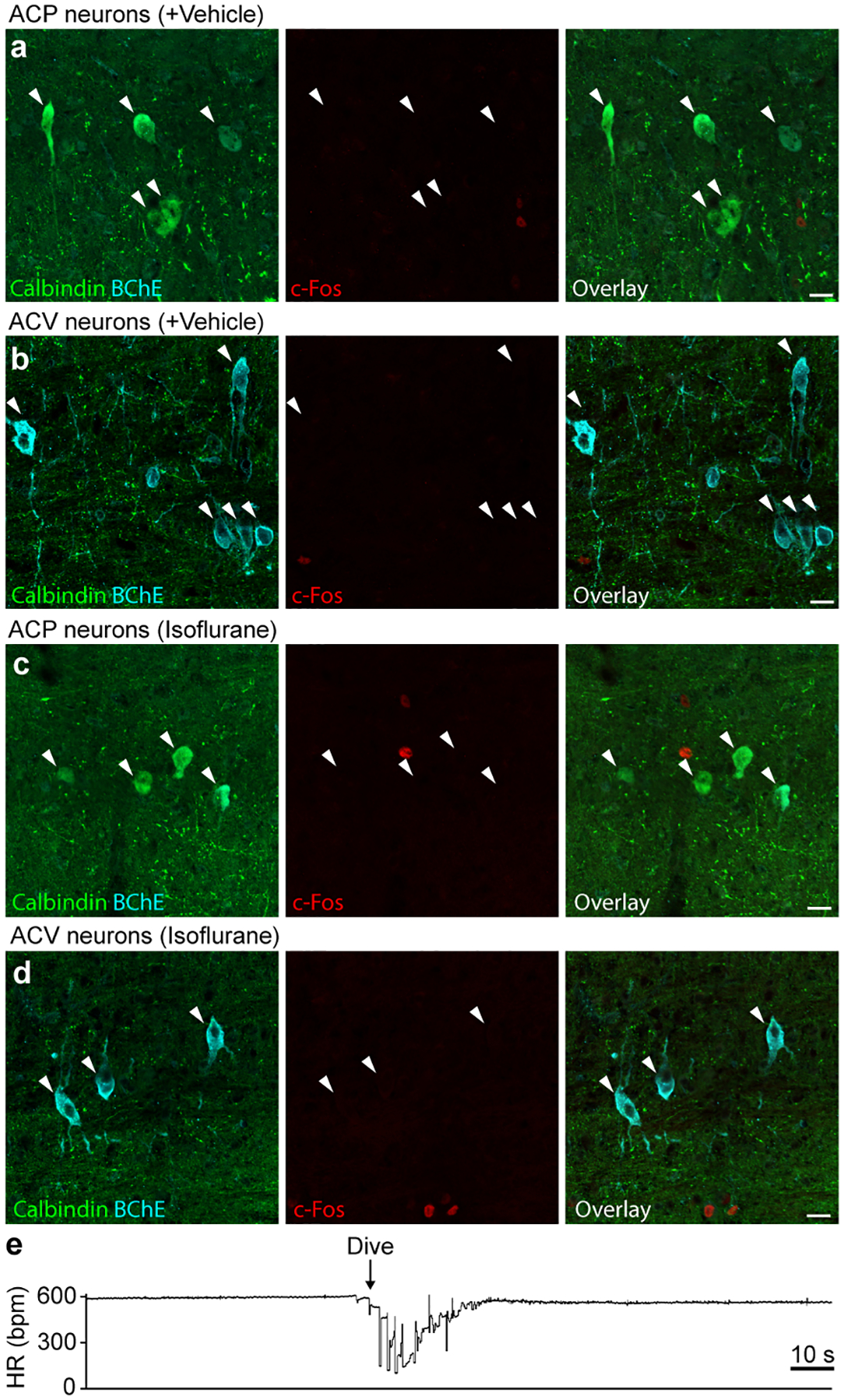
a, Immunostaining of ACP neurons in rostral Amb following vehicle injection (see Fig. 5). Note ACP neurons (calbindin+, white arrowheads) are c-Fos negative. b, Immunostaining of ACV neurons in caudal Amb following vehicle injection. Note ACV neurons (BChE+, white arrowheads) are c-Fos negative. c, Immunostaining of ACP neurons in rostral Amb following isoflurane anesthesia without nasal immersion. Note ACP neurons (calbindin+, white arrowheads) are c-Fos negative. d, Immunostaining of ACV neurons in caudal Amb following isoflurane anesthesia without nasal immersion. Note ACV neurons (BChE+, white arrowheads) are c-Fos negative. Bars, 20 μm. e, Example heart rate trace recorded by ECG during dive reflex activation for Fig. 5 experiments. Isoflurane-anesthetized mouse underwent nasal immersion (arrow, start of dive) for 10 s. Bradycardia and AV block were observed during nasal immersion, and heart rate returned to baseline following cessation of immersion.
