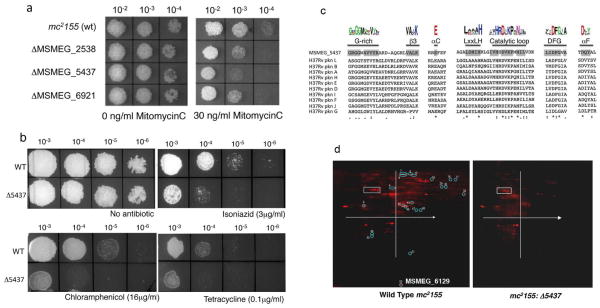
Figure 1. MSMEG_5437, a predicted STPK, is required for M. smegmatis tolerance to MitomycinC and antibiotics.
(a) Ten fold dilutions of gene replacement mutants in MSMEG_2538, MSMEG_5437 and MSMEG_6921 were spotted on Middlebrook 7H10 containing 30ng/ml of MMC with ΔMSMEG_5437 being the most sensitive of the mutants. (b) Ten fold serial dilutions of wild type and mc2155:Δ5437 were spotted on Middlebrook 7H10 containing indicated concentrations of isoniazid, chloramphenicol and tetracycline as well as a control lacking antibiotic. The mutant is hypersensitive to all three antibiotics tested. (c) Multiple sequence alignment of MSMEG_5437 with the eukaryotic like STPKs in M. tuberculosis showing the conserved signature motifs of bacterial ser/thr kinases and the conserved kinase domain in MSMEG_5437 shaded in grey. Deviations in the sequence of MSMEG_5437 are observed in the glycine rich motif and the catalytic loop and are marked. (d) Total cell lysate was prepared from wild type mc2155 and mc2155: Δ5437 and separated by 2-D gel electrophoresis. The gels were fixed and stained with a fluorescent phosphoprotein that stains all phosphorylated proteins. Differentially phosphorylated proteins were located using a combination of ImageQuant and DeCyder softwares. The white box and x and y_axis on each slide are for orientation purposes. Fifty one differentially phosphorylated proteins were identified and are circled and numbered. Twenty one protein spots were completely absent in mc2155: Δ5437 and were excised from the gel and identified by MALDI TOF/TOF (tandem mass spectrometry MS/MS). Identity of these spots is presented in Table 1.