Fig. 2.
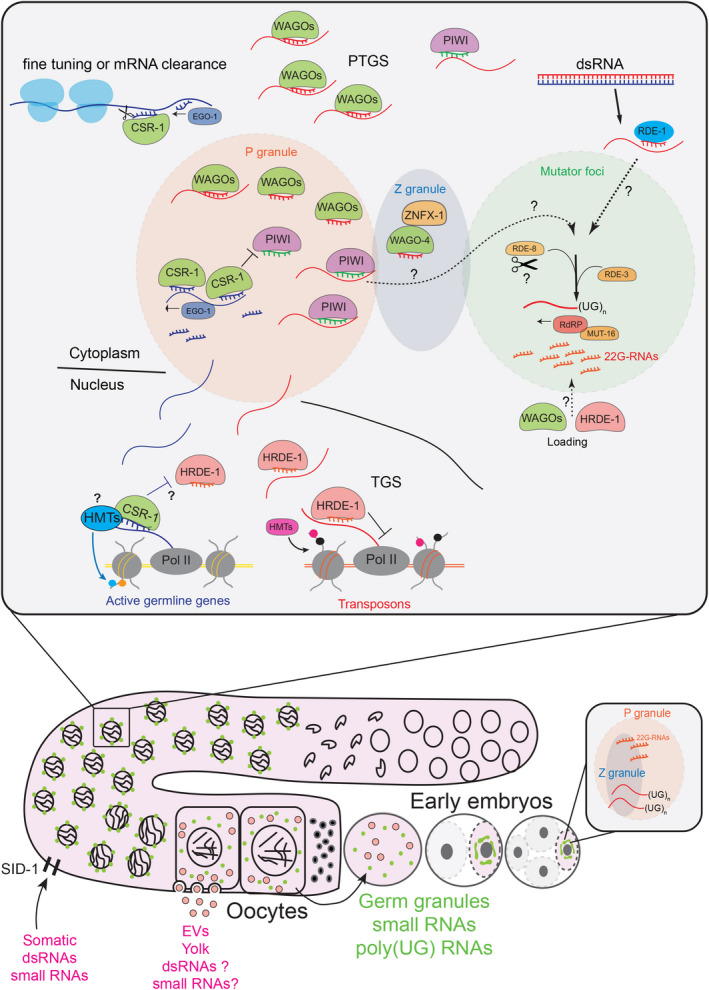
Schematic of the different endogenous germline small RNA pathways and their inheritance in C. elegans. Most of the Argonaute proteins localize to germ granules, phase‐separated condensates surrounding the nuclear membrane in the germline of C. elegans. Three different condensates characterize germ granules (P granules, Z granules, and mutator foci). The P granules contain most of the WAGOs, PIWI, and CSR‐1 proteins. The Z granules contain factors involved in heritable RNAi. The mutator foci include most of the enzymes required for the biogenesis of 22G‐RNAs triggered by dsRNAs or piRNAs. The 22G‐RNAs derived from active germline genes are produced by the RdRP EGO‐1 and are loaded into the Argonaute CSR‐1. These CSR‐1 22G‐RNAs can protect germline mRNAs from piRNA silencing and promote the degradation of the complementary mRNAs in the cytosol through the CSR‐1 catalytic activity. CSR‐1 can also bind nascent transcripts and prevent HRDE‐1 nuclear silencing. Most of the germline 22G‐RNAs and pUGylated mRNAs are transmitted to the embryos inside the germ granules. Somatic 22G‐RNAs and dsRNAs are transmitted to the germline through the dsRNA receptor SID‐1 or possibly through EVs carrying yolk protein from the intestine to the oocytes.
