Fig. 3.
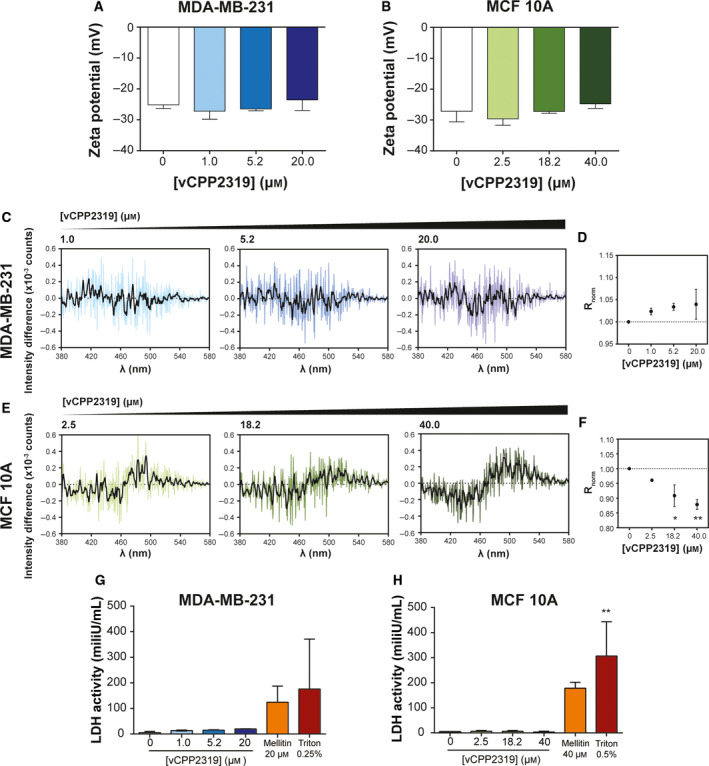
vCPP2319 interaction with human breast cell membranes. Zeta potential measurements of MDA‐MB‐231 (A) and MCF 10A (B) cells were performed in the absence (n = 13 and n = 8, respectively) and presence of vCPP2319, at increasing peptide concentrations (n = 2). The cell membrane dipole potential perturbation by vCPP2319 was studied by fluorescence spectroscopy using the fluorescent dye di‐8‐ANEPPS (C–F). The differential spectra were obtained by subtracting the normalized excitation spectra (to the integrated spectrum area) of the membrane‐inserted di‐8‐ANEPPS in the absence of vCPP2319 from the normalized excitation spectra of the membrane‐inserted di‐8‐ANEPPS in the presence of vCPP2319. A smoothened version of each differential spectrum is showed in each condition for clarity (C and E). The variation of the normalized excitation intensity ratios (R norm) with the increase in peptide concentration is also presented for MDA‐MB‐231 (D) and MCF 10A (F) cells (n = 2). This ratio enables for a better evaluation of the magnitude of membrane dipole potential perturbation. LDH activity was assessed in medium samples collected from untreated and treated MDA‐MB‐231 (G) and MCF 10A (H) cells (n = 2). Error bars refer to the standard deviation. Significance was assessed by ANOVA followed by Tukey’s (for zeta potential data) or Dunnett's post‐test. *P‐value ≤ 0.05; **P‐value ≤ 0.01.
