FIGURE 5.
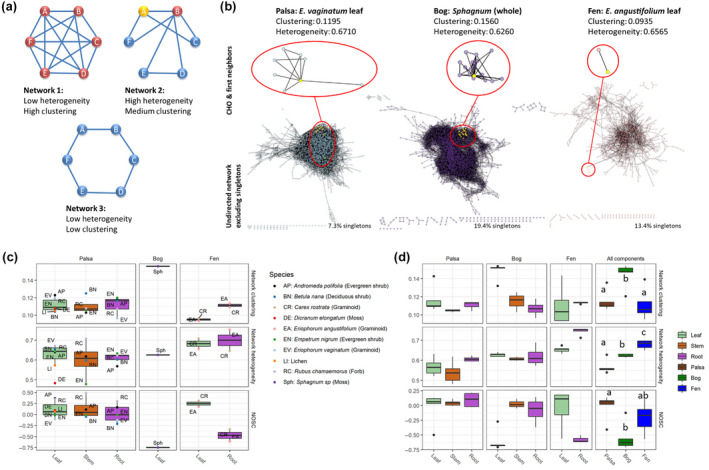
Plant chemistry network characteristics and NOSC. (a) Examples of networks with different clustering coefficients and heterogeneity, with nodes colored by the number of connecting edges (red = 5, yellow = 3, blue = 2). Network 1: all nodes are equally connected resulting in low heterogeneity and as connected as possible resulting in a high clustering coefficient. Network 2: Node B is a highly connected hub node while others have very few connections resulting in a high variance in connectivity across nodes (Dong & Horvath, 2007) which creates high heterogeneity and an intermediate clustering coefficient (since the average number of connections between nodes is neither maximal nor minimal). Network 3: All nodes are equally connected resulting in low heterogeneity, and the average number of connections between nodes is very low resulting in a low clustering coefficient. (b) Visualization of networks for litter used in incubations with peat from palsa (E. vaginatum leaf), bog (Sphagnum), and fen (E. angustifolium leaf). Zoomed‐in areas show sub‐networks for a single compound (CHO) and its first neighbors to illustrate differences in clustering and heterogeneity. (c) Differences in bioavailability of plant litter based on FT‐ICR MS analyses showing average nominal oxidation state of carbon (NOSC), network heterogeneity, and network clustering coefficient for each tissue type of each plant species grouped by permafrost thaw stage and tissue type. Both network heterogeneity and clustering coefficient have a possible range from 0 to 1, while NOSC may range from −4 to +4. (d) biomass‐weighted average NOSC, network heterogeneity, and clustering coefficient for each tissue type as well as total plant biomass (all components) at each thaw stage. Mass‐weighted indices were calculated based on biomass contribution per field‐sampling plot for each species. Variation within a thawing stage is driven by species composition differences between plots. Different letters indicate significant differences based on ANOVA and Tukey HSD tests with p < .05
