Figure 1.
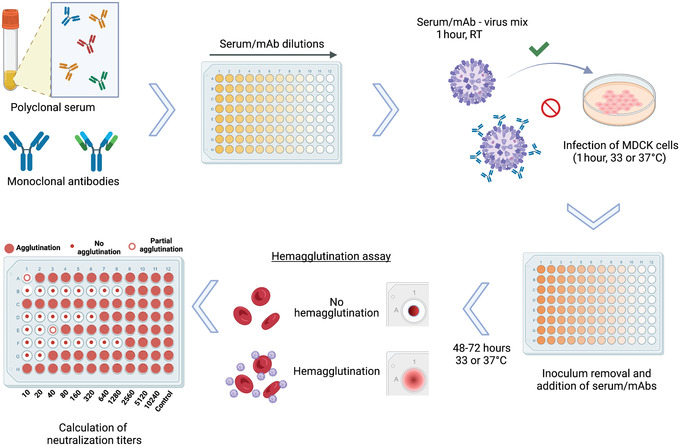
Overview of microneutralization assay for influenza virus serology. Antibodies in polyclonal serum samples of different origin, or monoclonal antibodies (mAb) in distinct configurations including chimeric antibodies, Fab fragments, and others, can be assessed for their neutralization capacity against different strains and subtypes of influenza virus. After dilution of samples, the virus to be tested is added at 100 TCID50/50 µl and incubated for 1 hr at room temperature (RT). The serum/mAb–virus mix is transferred to confluent MDCK cells and incubated for 1 hr at 33° or 37°C, depending on the virus strain used. After inoculum removal, serum samples diluted in infection medium are added to the plates and incubated for 48‐72 hr at 33° or 37°C. A hemagglutination assay is performed to detect the presence of virus in cell supernatants and to calculate neutralization titers. Reciprocal titers (1:x serum dilution) are displayed as absolute values.
