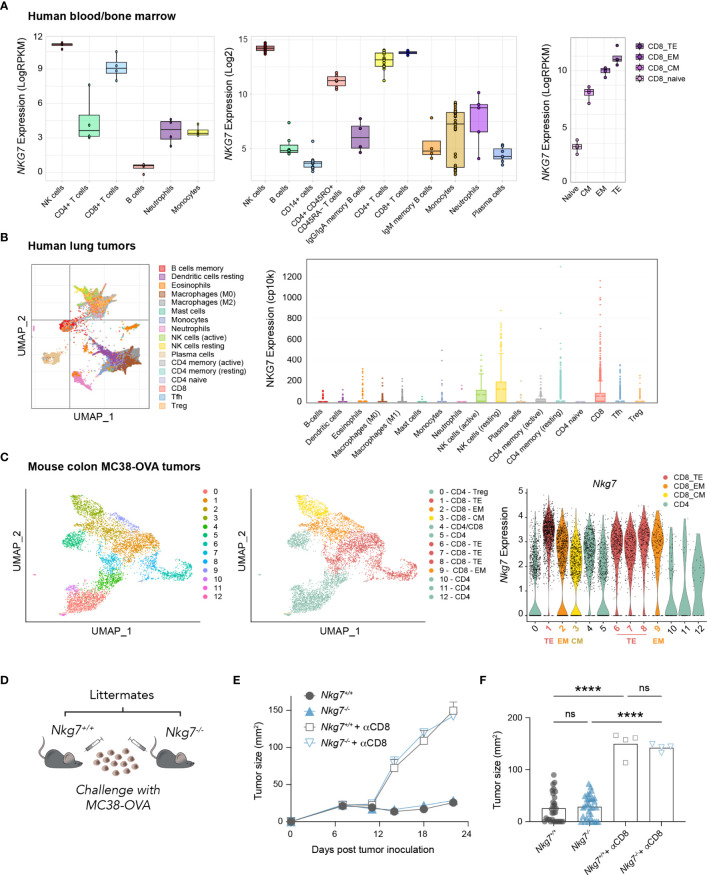
Figure 1.
NKG7 is highly expressed in tumor-infiltrating CD8+ effector T cells but is not required for CD8+ T cell-mediated control of MC38-OVA tumors in vivo. (A–C) Analysis of bulk and single-cell RNA-seq and CITE-seq datasets available through the GEO. TE – Terminal Effector; EM – Effector Memory; CM – Central Memory (A) Bulk RNA-seq showing NKG7 expression on sorted cells from healthy human donor whole blood (left panel; GSE60424 (30), PBMCs or bone marrow (middle panel; GSE22886 (31), and PBMCs (right panel; GSE107011 (29). (B) Single cell RNA-seq showing NKG7 expression across different tumor-infiltrating immune subsets in human lung carcinoma (GSE127465 (32). (C) Single cell CITE-seq showing Nkg7 expression in tumor infiltrating T cells from MC38-OVA tumors harvested 10 days post subcutaneous tumor inoculation in C57BL/6 mice (GSE182664 (14). (D) Schematic of in vivo tumor growth study. MC38-OVA cells were implanted subcutaneously in Nkg7+/+ or Nkg7-/- littermates with or without CD8 depletion antibodies administered starting the day prior to tumor inoculation. (E) Tumor growth, error bars show SEM. (F) Tumor size on day 22 post tumor inoculation, data is pooled from 4 independent experiments, One-way ANOVA (n = 4-31). ns – not significant, **** P <0.0001.