Figure 1.
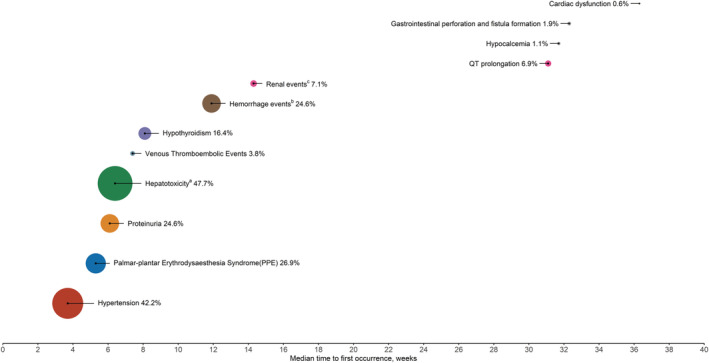
Incidence (%) and median time to onset of selected adverse events in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with lenvatinib. Based on available data from clinical trials, 9 , 10 the size of the circle is proportional to the incidence. aHepatotoxicity includes blood bilirubin increase, ascites, AST/ALT increased, hypoalbuminemia, hepatic encephalopathy, gamma‐glutamyltransferase increase, hepatic failure, hepatic function abnormal, hyperbilirubinemia, hyperammonemia, jaundice cholestatic, hepatic pain, jaundice, urine bilirubin increased, hepatic cirrhosis, coma hepatic, edema due to hepatic disease, varices esophageal, and portal hypertensive gastropathy. bMost frequently reported hemorrhage events were epistaxis, hematuria, and gingival bleeding. Grade ≥ 3 events occurred in 24 subjects (5.0%) in the lenvatinib arm. cThe most frequently reported renal events were blood creatinine increased, acute kidney injury, and renal impairment. Grade ≥ 3 events occurred in 9 subjects (1.9%) in the lenvatinib arm.
