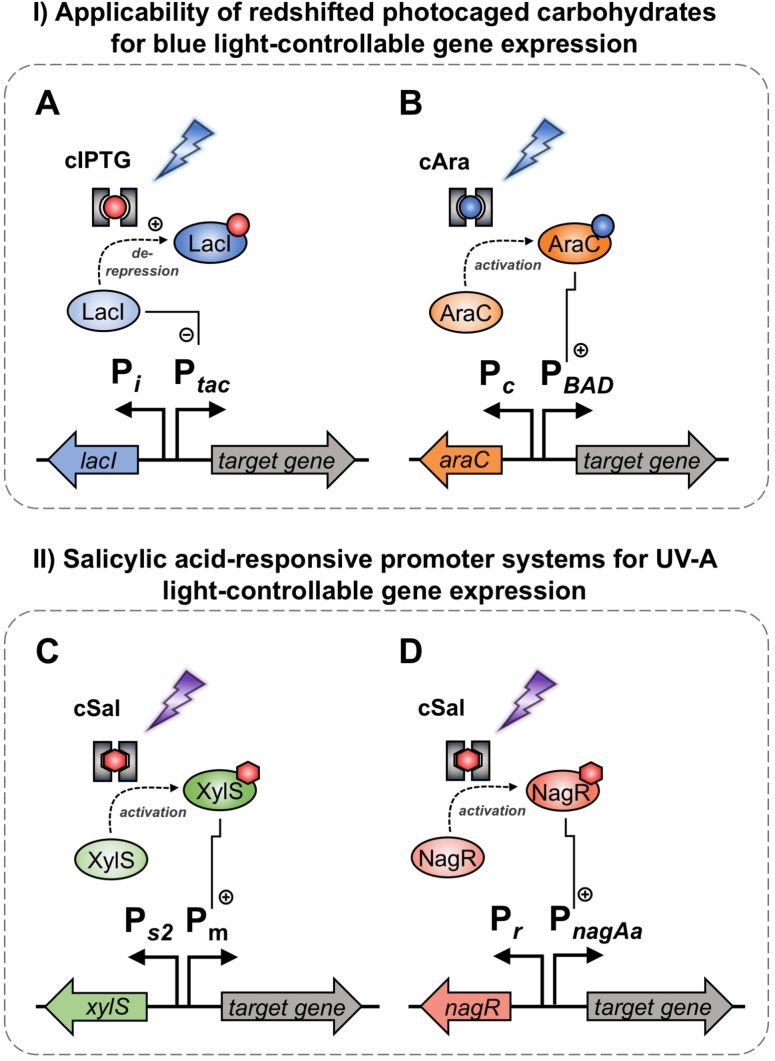
Figure 1.
Promoter systems for optogenetic control of target gene expression used in this study. Firstly, the applicability of photocaged carbohydrates for controlling gene expression with blue light (flash symbol) was evaluated. For induction with photocaged IPTG (cIPTG, red dot with grey frame), the well‐established P tac /LacI promoter system (A) was chosen, in which the P tac promoter is subject to regulation by the LacI activator protein. Upon binding of a suited inducer such as IPTG (red dot), LacI undergoes a conformational change leading to the dissociation from the operator region and thus, de‐repression of transcription. For induction with photocaged arabinose (cAra, blue dot with grey frame), the P BAD /AraC promoter system (B) was applied, which is positively regulated by the activator protein AraC upon l‐arabinose (blue dot) binding. As a second step, salicylic acid‐responsive promoter systems were for the first time evaluated for photo‐controllable gene expression using photocaged salicylic acid derivatives (cSal, red hexagon with grey frame). For this purpose, the P m /XylS regulatory system was applied, which is positively controlled by the activator protein XylS in the presence of salicylic acid (red hexagon). Furthermore, the P nagAa /NagR regulon was evaluated, which is also positively regulated by its activator protein NagR in the presence of salicylic acid (red hexagon).