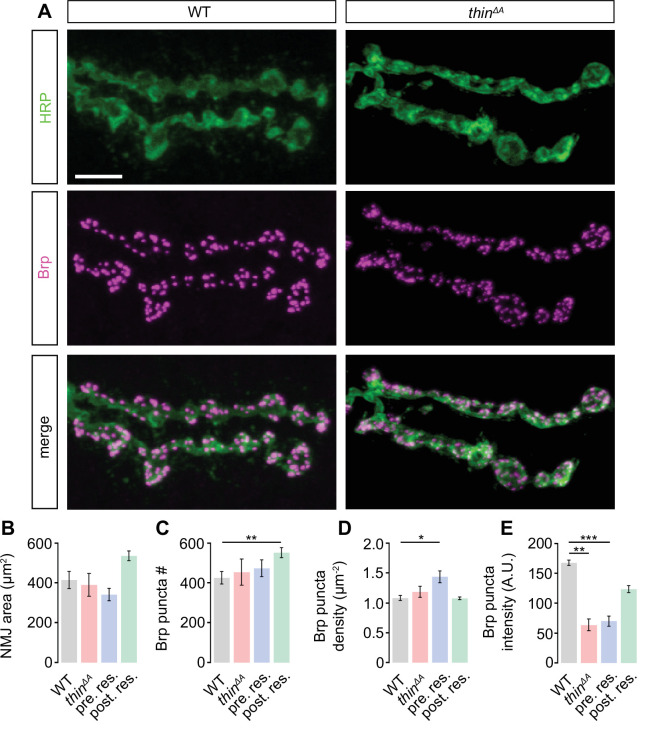
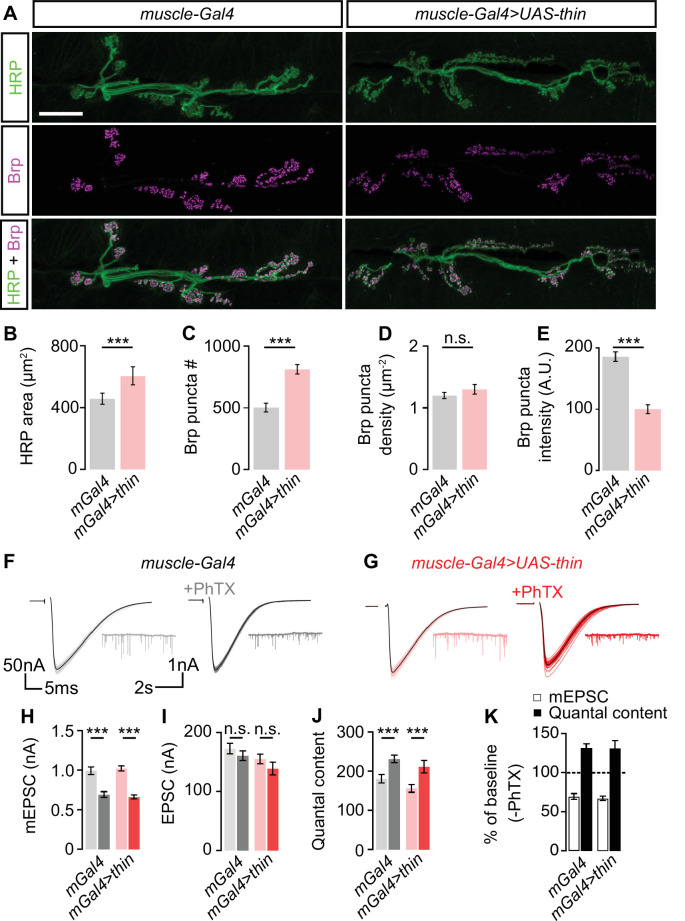
(A) Maximum intensity projection of a control (24B-Gal4/+, ‘muscle-Gal4’, left and 24B-Gal4>UAS thin, ‘muscle-Gal4>UAS-thin’, right) neuromuscular junction (NMJ) (muscle 6) stained against the Drosophila neuronal membrane marker anti-HRP (‘HRP’) and the active-zone marker Bruchpilot (‘Brp’); scale bar, 20µm. Mean HRP area per NMJ (‘HRP area’) (B), Brp puncta number per NMJ (‘Brp puncta #’) (C), Brp puncta number/HRP area per NMJ ‘Brp density’ (D), and Brp puncta fluorescence intensity (E) of the indicated genotypes. 24B-Gal4/+: n = 10; 24B-Gal4>UAS-thin: n = 12. (F) Representative excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) (individual sweeps and averages are shown in light colors and black, respectively), and mEPSCs (insets) of a control NMJ (24B-Gal4/+, ‘muscle Gal4’) in the absence (light gray) and presence of philanthotoxin-443 (PhTX) (‘+PhTX’, dark gray). Stimulation artifacts were blanked for clarity. (G) Same as in (F) for an NMJ overexpressing thin in the muscle (24B-Gal4>UAS thin, ‘muscle-Gal4>UAS-thin’). Mean mEPSC amplitudes (H), EPSC amplitudes (I), and quantal content (J) of control (24B-Gal4/+, ‘mGal4’, gray) and postsynaptic thin overexpression (24B-Gal4>UAS thin, ‘mGal4 >thin’, red) without (light colors) and after PhTX treatment (dark colors). (K) mEPSC amplitude (white) and quantal content (black) in the presence of PhTX normalized to control (without PhTX) of the indicated genotypes. PhTX treatment increased quantal content after postsynaptic thin overexpression, indicating PHP expression. Postsynaptic thin overexpression did not change baseline miniature excitatory postsynaptic potential (mEPSP) or EPSC amplitude. The increase in HRP area (B), Brp number (C), or the decrease in Brp intensity (E) upon postsynaptic thin overexpression thus do not translate into apparent changes in PHP or baseline synaptic transmission. Mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM); 24B-Gal4/+ − PhTX: n = 16, 24B-Gal4/++PhTX: n = 17; 24B-Gal4>UAS thin − PhTX: n = 13, 24B-Gal4>UAS thin + PhTX: n = 23; ***p < 0.001; n.s.: not significant; Student’s t-test for pairwise comparison between control (24B-Gal4/+) and postsynaptic thin overexpression (24B-Gal4>UAS thin).
Figure 3—figure supplement 1—source data 1. Related to Figure 3—figure supplement 1.Postsynaptic thin expression does not affect presynaptic homeostatic plasticity (PHP) or baseline synaptic transmission.