Fig. 7.
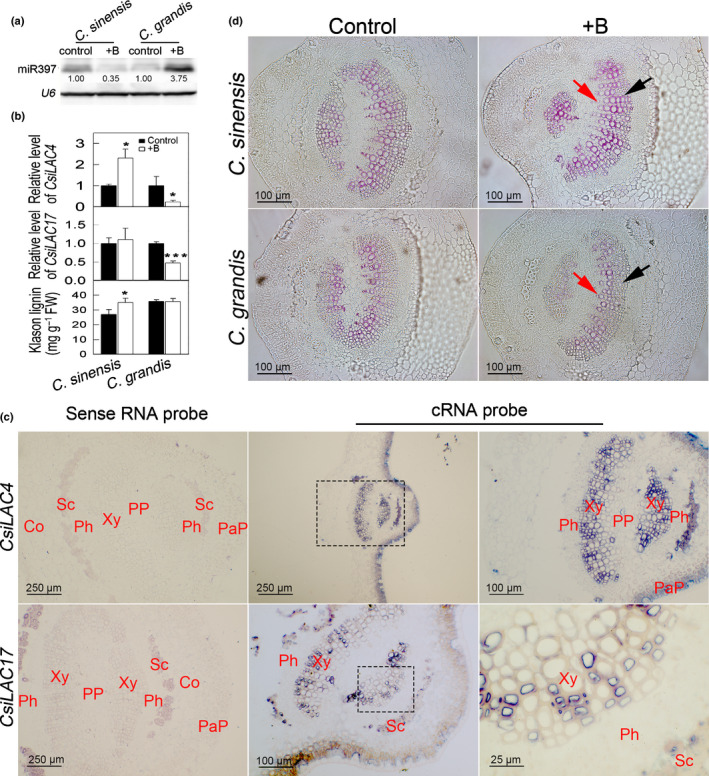
Boric acid (BA)‐responsive miR397 in Citrus leaves negatively modulates CsiLAC4, which contributes to lignification of the metaxylem parenchyma. (a) miRNA blotting. miR397 levels in BA‐treated Citrus sinensis and Citrus grandis leaves. (b) Relative levels of CsiLAC4 and CsiLAC17 and Klason lignin content in responding to excessive BA treatments. (c) In situ mRNA hybridization showed that CsiLAC4 and CsiLAC17 are specifically expressed in the metaxylem. (d) BA treatment results in lignin deposition in the metaxylem according to phloroglucinol‐HCl staining. Co, cortex; PaP, palisade parenchyma; Ph, phloem; PP, pith parenchyma; Sc, sclerenchyma; Xy, xylem. Black arrows indicate the metaxylem, while red arrows indicate the protoxylem. Results are mean ± SD. Asterisks indicate significant differences at: *, P < 0.05; and ***, P < 0.001 by independent sample t‐tests (n = 3).
