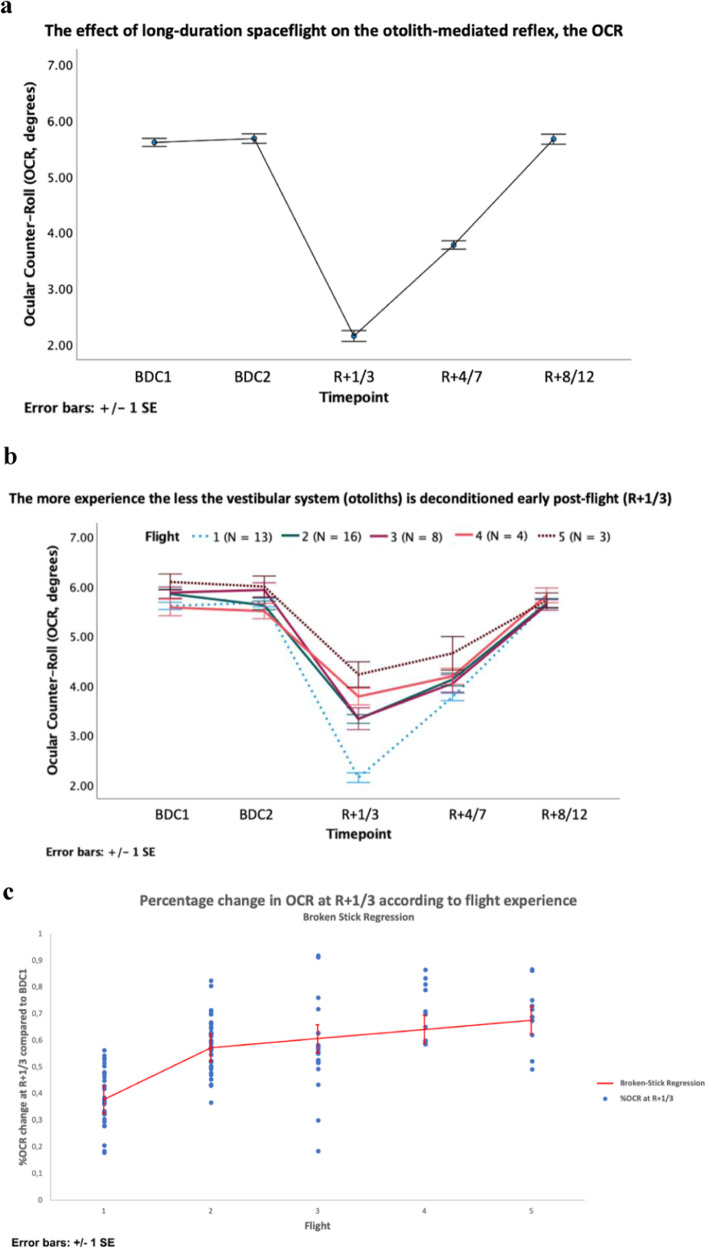
Fig. 6. The effect of long-duration spaceflight and spaceflight experience on the otolith-mediated reflex, the OCR.
a The effect of spaceflight on the otolith-mediated reflex, the ocular counter-roll (OCR). The overall average (including both eyes and centrifugation directions) of the OCR measurements at CD2 for the first-time flyers show a decreased OCR early postflight (R + 1/3) after a 6-month space mission. In addition, the evolution of the OCR across the first 2 weeks postflight is illustrated, showing a return to BDC levels 8–12 days after their return. b The difference between 1st-, 2nd-, 3rd-, 4th-, and 5th-time flyers regarding the effect of long-duration spaceflight on the otolith-mediated OCR. All flyers (first-time to frequent flyers) show a clear decrease in early postflight (R + 1/3). However, the more the cosmonauts have flown the less the OCR gain is decreased postflight. For each flier, the OCR measurement at CD2 is represented as an average of both centrifugation directions and eyes. c Percentage change in OCR at R + 1/3 according to the flight experience. Piecewise linear regression. BDC baseline data collection, R + X return after X days. Error bars of the three graphs represent standard error of mean with multiplier one.