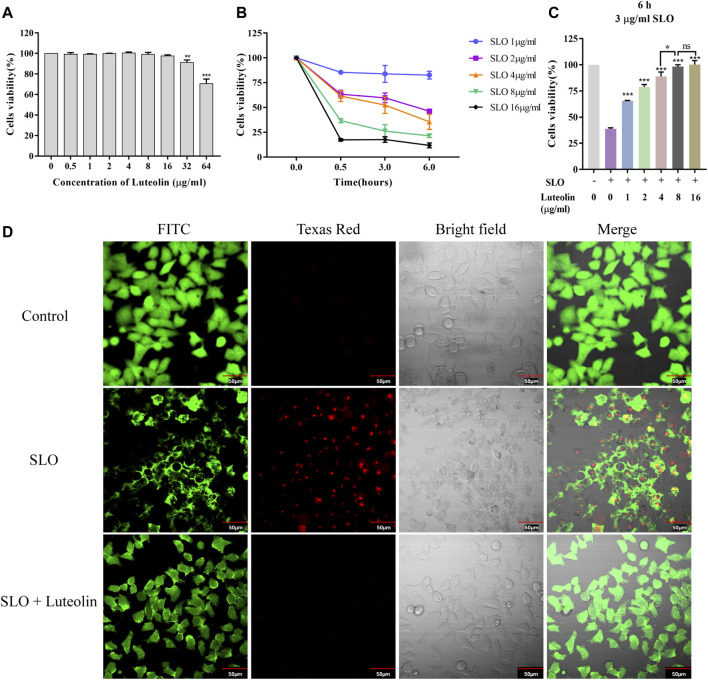
FIGURE 5.
Effect of Luteolin on SLO toxin-mediated pathology in human HEp-2 cells. (A) Cytotoxicity of luteolin for 24 h. (B) Dose-response and time-course experiments to evaluate SLO cytotoxic effects in HEp-2 cells. Cells were treated with SLO at concentrations of 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16 μg/ml for 0, 0.5, 3, and 6 h, respectively. Cell viability was determined by the CCK-8 assay, and the cell viability of the untreated group was defined as 100%. Data represent the mean value ± SD derived from three replicates. (C) HEp-2 cells were treated for 6 h with 3 μg/ml of SLO, in the absence or presence of luteolin. The cell viability was determined by the CCK-8 assay, and the cell viability of the untreated group was defined as 100%. Data represent the mean value ± SD derived from three replicates (Two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post test). *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001, with ns. used to indicate results were not significant. (D) HEp-2 cells were treated with 3 μg/ml of SLO, in the absence or presence of luteolin (8 μg/ml), for 6 h. Cells were stained with FITC fluorescent cell dye solution (green signal) to visualize living cells. Texas Red staining, which mainly produces nuclear red fluorescence in cells with damaged cell membranes, was used to visualize damaged cells.