Figure 1.
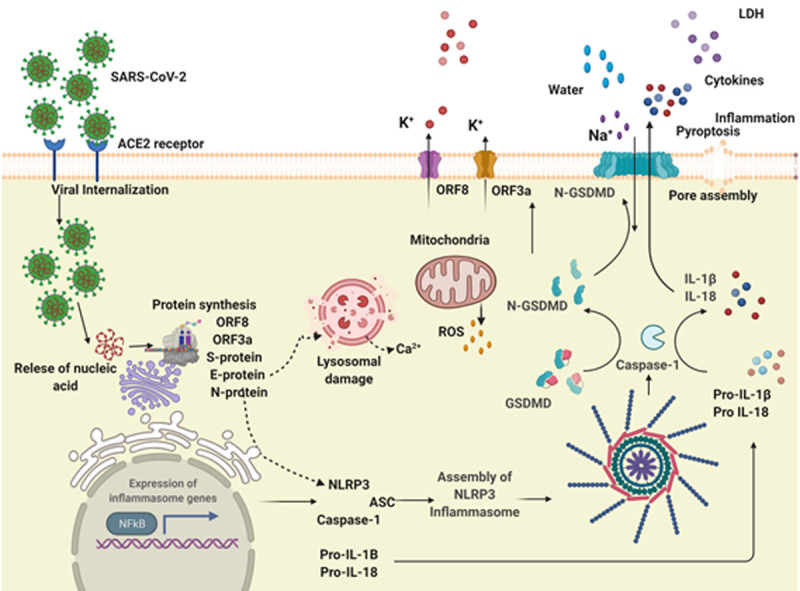
Activation of NLRP3 inflammasome by SARS-CoV-2. SARS-CoV-2 infection occurs by binding of Spike glycoprotein with cell surface receptor ACE2 leading to viral internalization, followed by the release of nucleic acid, viral replication and synthesis of viral proteins. Infection of SARS-CoV-2 upregulates the NFkB pathway leading to increased expression and synthesis of NLRP3 and IL-1β. Viral proteins including S, N, E and viroporins interact with NLRP3 and facilitate inflammasome assembly via oligomerization, the interaction of NLRP3 with ASC and cleavage of caspas1 leading to maturation and release of IL-18 and IL-1β. Ion channels and ion flux are also involved in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Mitochondrial ROS and lysosomal degradation further impart NLRP3 inflammasome activation.
