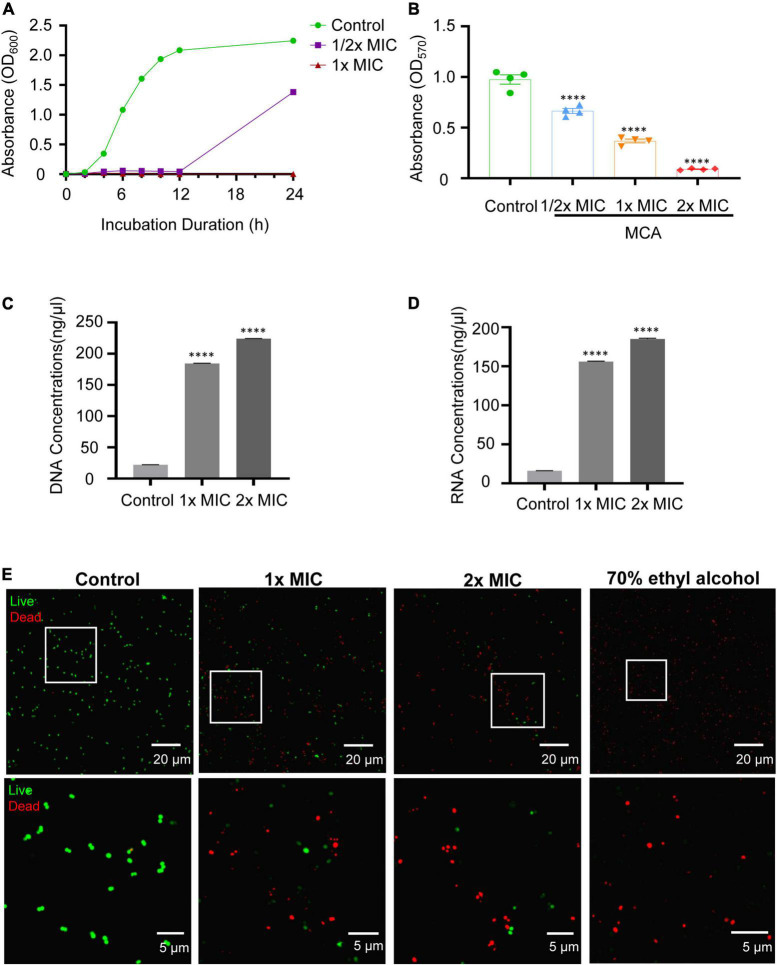
FIGURE 1.
MCA inhibited the growth and biofilm formation, and increased the permeability of MRSE. (A) MCA inhibited the proliferation of MRSE in a dose-dependent way. MRSE in the exponential growth phase was treated with MCA at 0, 1/2× MIC, and 1× MIC for the indicated time, respectively, while 0.1% EtOH was used as the vehicle control. The proliferation of MRSE was measured by monitoring the absorbance at 600 nm (OD600). (B) MRSE inhibited biofilm formation of MRSE. MRSE in the exponential growth phase was treated with MCA at the indicated concentration for 24 h, and the biofilm formation was measured by monitoring the absorbance at 570 nm (OD570) after CV staining. (C,D) MCA induced the leakage of DNA and RNA from MRSE. MRSE in the exponential growth phase was treated with MCA at 1× MIC and 2× MIC for 6 h, while the 0.1% EtOH was used as vehicle control. The leakages of DNA and RNA were quantified by measuring the absorbance at 260 and 230 nm using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer. The pooled data are presented as mean ± SEM of at least three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. (E) MCA decreased the viability of MRSE. MRSE was treated with MCA at the indicated concentration for 6 h and then stained with SYTO-9/PI. The images were obtained by confocal microscopy, and the green and red fluorescence indicate the live and dead bacteria, respectively. The highlighted regions are magnified in the lower panel. The representative images were selected from at least three independent experiments.