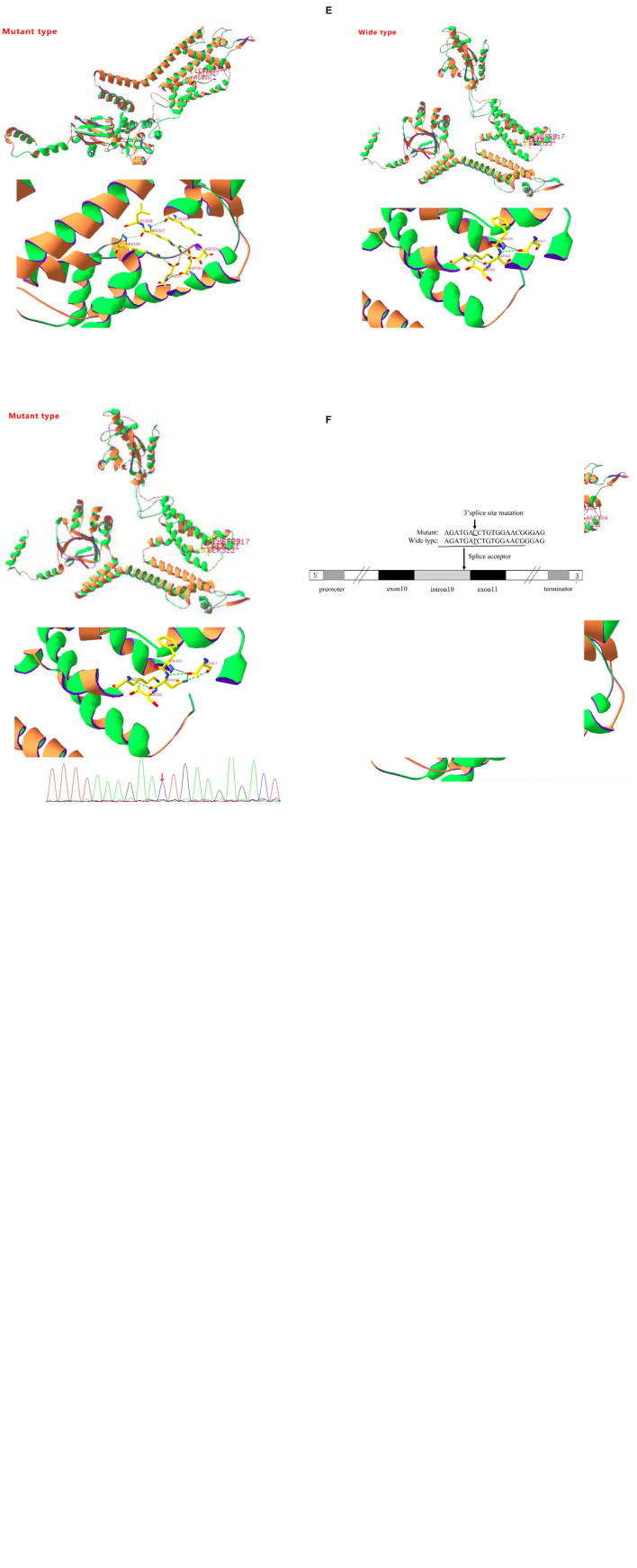
FIGURE 1.
(A) Sanger sequencing results of the KCNH5 gene in the case 1 family. One mutation of KCNH5 was identified in this patient, which was c.980G > A (Red arrow). The parents are normal. (B) Sanger sequencing results of the KCNH5 gene in the case 2 family. One mutation of KCNH5 was identified in this patient, which was c.2020-4A > G (Red arrow). The parents are normal. (C) Sanger sequencing results of the KCNH5 gene in the case 3 family. One mutation of KCNH5 was identified in this patient, which was c.962G > A (Red arrow). The parents are normal. (D,E) Mutation analysis and models of the predicted protein structure of KCNH5. (A–C) Show the mutations in the patients and their parents, as confirmed by Sanger sequencing. (D) Shows the 3D structure of KCNH5 in case one (c.980G > A). The green dotted line indicates hydrogen bonds between groups. The solid yellow line represents the covalent bonds. In the wild type, the main body of Arg327 is connected to LYS324 and Arg330 by hydrogen bonds, and the side chain of Arg327 is connected to Asp304, Asp251, and Asp255 by hydrogen bonds. In the mutant type, the main body of His327 is connected to LYS324 and Arg330 by hydrogen bonds, and the side chain of His327 is connected to Arg330 by hydrogen bonds. (E) Shows the 3D structure of KCNH5 in case 3 (c.962G > A). In the wild type, the main body of Ser321 is connected to LYS324 and Ser317 by hydrogen bonds. In the mutant type, the main body of Asn321 is connected to LYS324 and Ser317 by hydrogen bonds, and the side chain of Asn321 is connected to Ser317 by hydrogen bonds. (F) The mutation are of case 2.