Fig. 1.
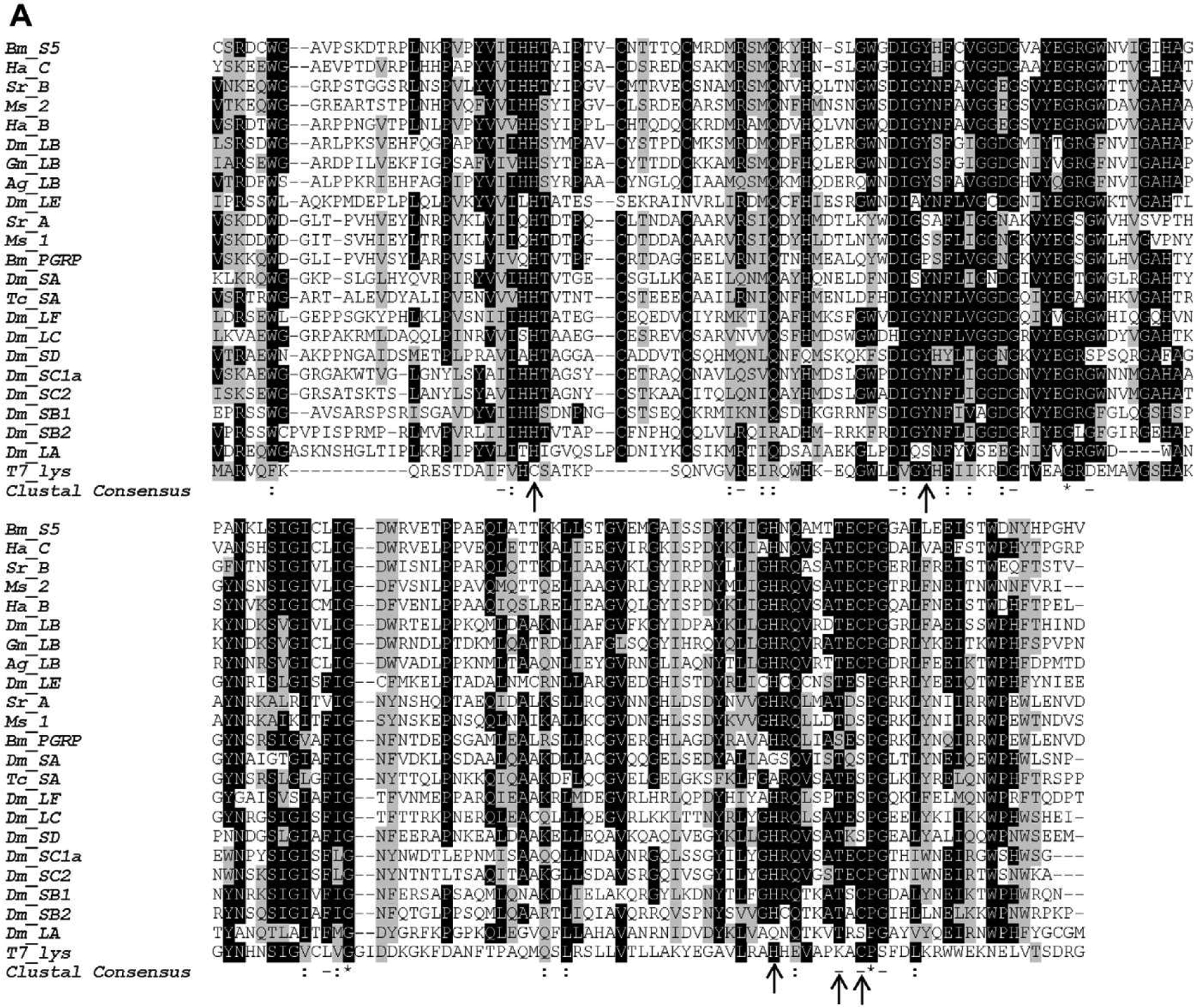

Multiple PGRP sequence alignment using ClustalW (A) and construction of phylogenetic tree (B). Identical and similar amino acid residues are shaded in black and gray, respectively. The residues responsible for zinc binding and amidase are indicated with arrows. The scale bar on the bottom of the tree indicates the distance. Numbers on the branches represent the distances. Bm, B. mori (PGRP-S5: NP_001036858.1; PGRP: BAA77209); Ha, Helicoverpa armigera (PGRP-B: AFP23116; PGRP-C AFP23117); Sr, Samia Cynthia ricini (PGRP-A: BAF03522; PGRP-B: BAF03520); Ms, M. sexta (PGRP-1: AF413068; PGRP-2: ACX49764); Dm, D. melanogaster (PGRP-LA: CG32042; PGRP-LB: CG14704; PGRP-LC: CG4432; PGRP-LE: CG8995; PGRP-LF: CG4437; PGRP-SA: CG11709; PGRP-SB1: CG9681; PGRP-SB2: CG9697; PGRP-SC1a: CG14746; PGRP-SC2: CG14745; PGRP-SD: CG7496); Gm, Glossina morsitans (PGRP-LB: ABC25064); Ag, Anopheles gambiae (PGRP-LB: XP_003435776); Tc, Tribolium castaneum (PGRP-SA: XP_969883).
