Figure 4.
Evaluation of AT domain hydrolytic activity
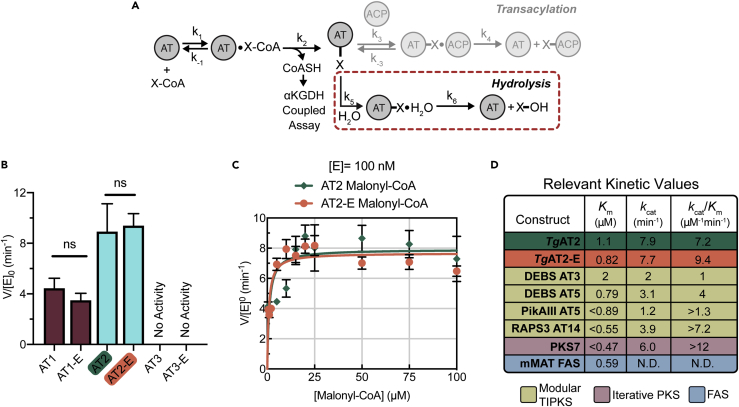
(A) Schematic of the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (αKGDH)-coupled kinetic assay used to assess AT domain hydrolysis activity.
(B) Relative rates of hydrolysis between TgPKS2 AT and AT-E domains with malonyl-CoA (150 μM). Significance determined using an unpaired t-test; ns, not significant. Data shown as the average ±standard error of the mean of 3 (AT2/AT2-E and AT3/AT3-E) or 4 (AT1/AT1-E) replicate measurements.
(C) Michaelis-Menten saturation curves for TgPKS2 AT2 (green) and AT2-E (orange) in the presence of malonyl-CoA. Data shown as the average ± standard error of the mean of triplicate measurements. Plots displaying lower concentrations shown in Figures S4F and S4G.
(D) Table of kinetic values for the rates of hydrolysis from this study (TgAT2/TgAT2-E) compared to known kinetic values for other modular type I PKS AT domains as well as from bacterial iterative PKS and FAS systems.