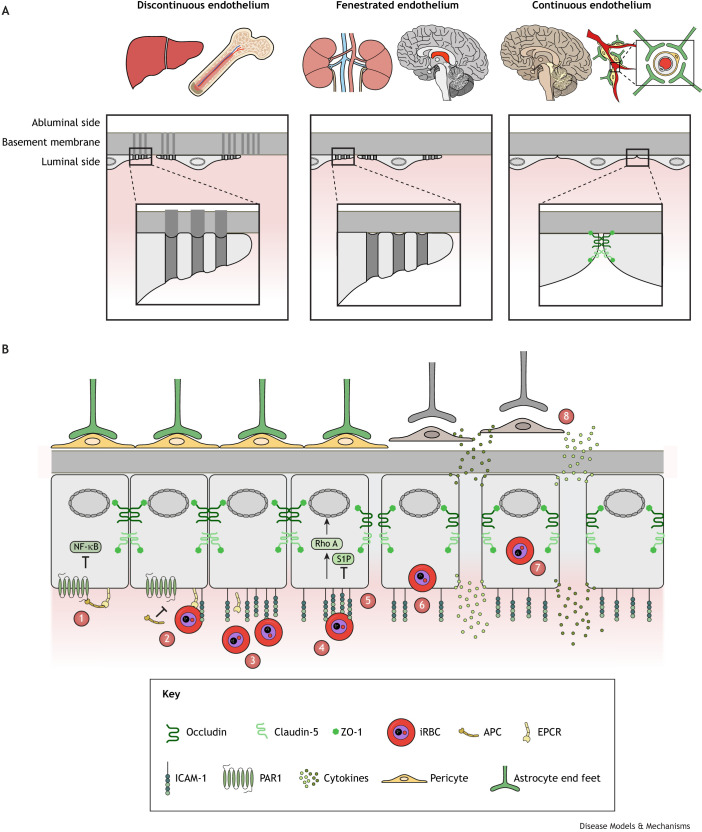
Fig. 1.
Types and functions of the endothelium. (A) Schematic of different types of endothelia found in the human body. Discontinuous endothelia are found in the liver sinusoids and bone marrow, and feature larger openings in the cells, typically 60-180 nm in diameter, which extend through the basement membrane. Fenestrated endothelia are found in the glomeruli of the kidneys and the choroid plexus in the brain (red). The fenestrations (pores) within the endothelial cells are typically 60-80 nm in diameter. Continuous endothelia form the blood–brain barrier (BBB) and are characterised by tight junctions between cells and highly selective transport of molecules. (B) The integrity of the continuous endothelium of the BBB can be compromised when P. falciparum-iRBCs bind to endothelial cell surface receptors. (1) In healthy endothelia, APC can bind to PAR1 (also known as F2R), inhibiting NF-κB and ensuring a cytoprotective state. ZO-1, claudin-5 and occludin combine to form tight junctions to help maintain barrier integrity. (2) iRBCs capable of binding to both ICAM-1 and EPCR outcompete APC, triggering a pro-inflammatory state within endothelial cells, leading to a loss of EPCR surface expression (Moxon et al., 2013). (3) iRBCs can bind to ICAM-1, which is upregulated in malaria (Tripathi et al., 2006) and (4) which clusters around bound iRBCs (Adams et al., 2021). (5) This binding to ICAM-1 and clustering inhibits the production of sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) whilst triggering Rho A, which induces NF-κβ. Combined, this results in a loss of the tight junctions and barrier integrity. This is exacerbated further when (6) iRBCs enter the endothelial cells, further destabilising the barrier and resulting in (7) cytokine/chemokine release and the production of microparticles. This pro-inflammatory state of the endothelial cells, coupled with increased permeability, triggers an inflammatory cascade that disrupts the neurovascular unit by loosening tight junctions, (8) causing pericyte dysfunction and retraction of astrocyte end feet. This non-functional BBB cannot adequately protect the brain. APC, activated protein C; EPCR, endothelial protein receptor C; ICAM-1, intercellular adhesion molecule 1; iRBC, infected red blood cell; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; PAR1, protease-activated receptor 1; Rho A, ras homolog family protein A; S1P, sphingosine-1-phosphate; ZO-1, zonula occludens protein 1.