Extended Data Fig. 1. PIWI protein purification and extended PIWI family tree.
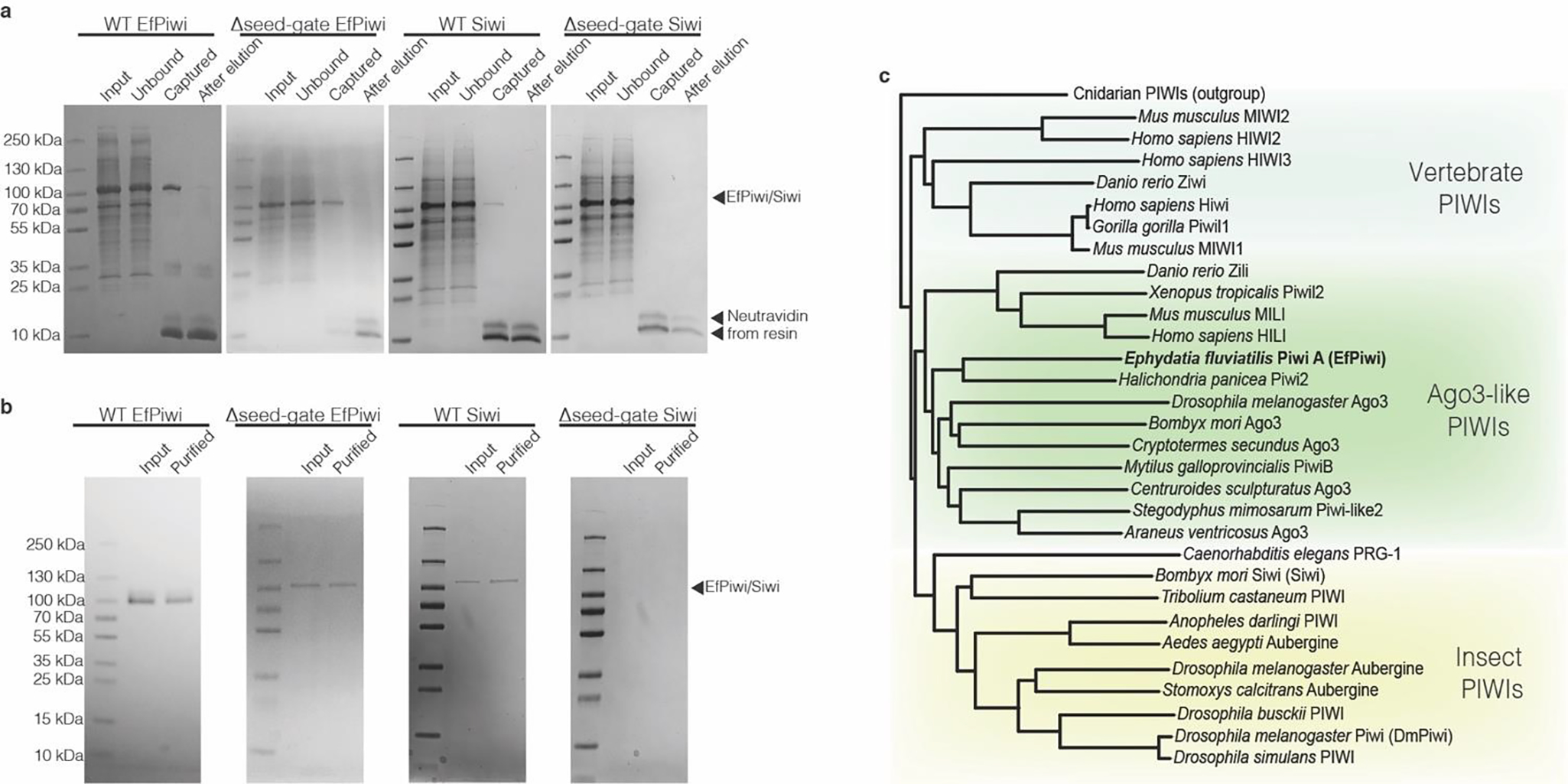
a, Coomassie-stained SDS PAGE of piRNA-loaded PIWI proteins captured using an immobilized complementary oligonucleotide. Input shows partially purified protein samples that were incubated with capture resin. Unbound shows protein that did not bind the resin. Captured shows protein retained on the resin after washing (eluted by boiling in SDS). After elution shows protein retained on the resin after incubation with the competitor oligonucleotide (eluted by boiling in SDS). b, capture-purified PIWI proteins before and after anion exchange purification. Input fraction shows samples after elution by competitor oligonucleotide in capture-purification step. Purified indicates the final purification products. Note: Δseed-gate Siwi was captured at such low levels that it was unclear whether any active Siwi was obtained until observing the sample’s ability to specifically bind 32P-labeled target RNAs. c, phylogenetic tree of PIWI proteins shows EfPiwi belongs to the ancient Drosophila AGO3-like branch.
