Extended Data Fig. 3. Conserved structural features in extended PIWI family.
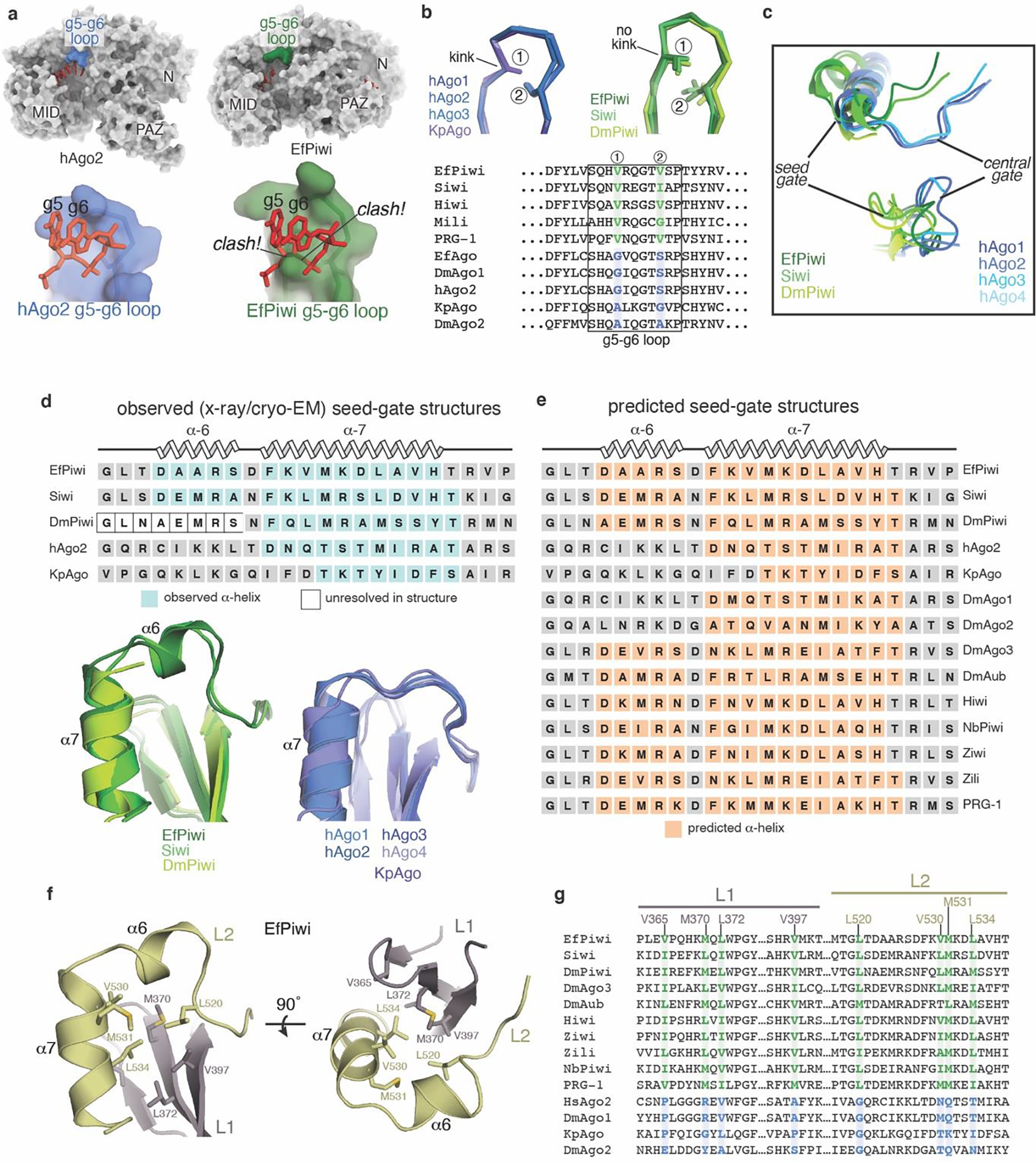
a, Surface of hAgo2 (left) and EfPiwi (right), highlighting g5-g6 nucleotide-binding loops. Superimposing g5-g6 nucleotides (red sticks) from hAgo2 onto EfPiwi results in steric clashes. b, g5-g6 loop in AGO structures (left) is kinked, enabling pre-organization of seed 3’ end. Equivalent loop in PIWI structures (right) cannot kink due to bulky residues (labeled positions 1 and 2), conserved in PIWI family. c, Close up superposition of central-gate and seed-gate structures in AGO and PIWI proteins, respectively. d, Superposition of seed-gate regions from all known PIWI (left) and AGO (right) structures, with secondary structure schematics shown above. e, Secondary structure predictions indicate the α6 extension is a defining feature of the PIWI family. Predictions were by PSIPRED 4.0. f, L1-L2 interface near seed-gate in EfPiwi. Hydrophobic residues buried at the L1-L2 interface are shown. g, Sequence alignment shows L1-L2 interface residues in EfPiwi are broadly conserved in PIWIs (green) and distinct from the equivalent residues in AGOs (blue).
