FIG 4.
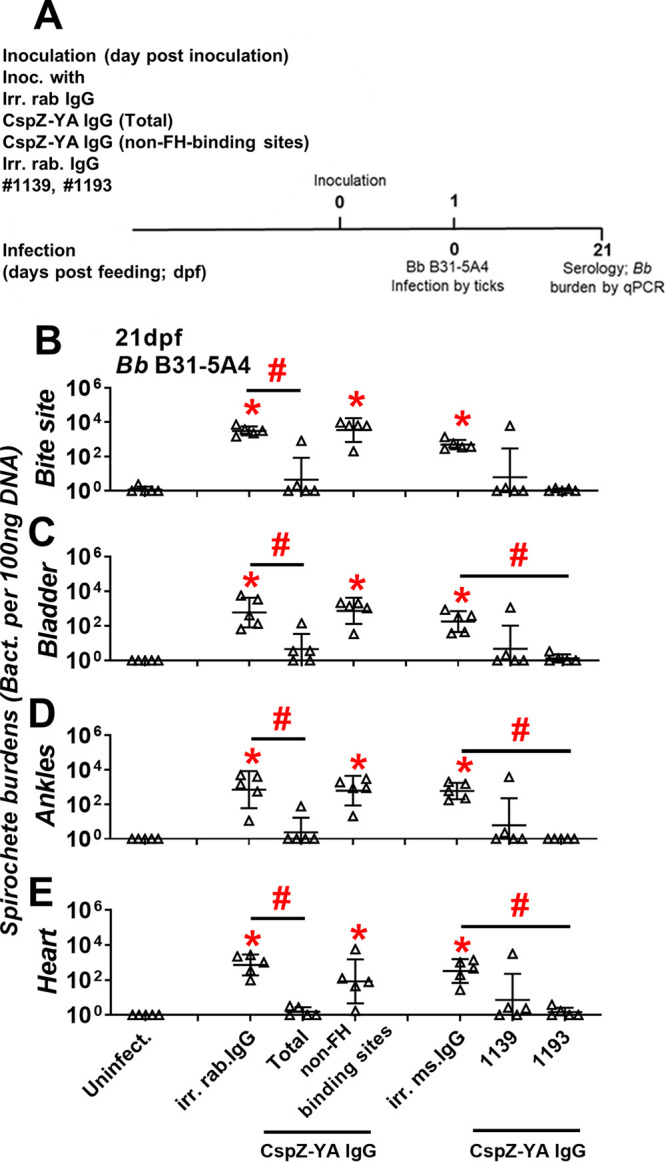
CspZ-YA IgGs that recognize CspZ FH-binding sites selectively prevent B. burgdorferi B31-5A4 infection. (A) Timeframe of the IgG inoculation and B. burgdorferi infection. (B to E) C3H/HeN mice were inoculated with irr. IgG from rabbits (irr. rab. IgG) or mice (irr. ms. IgG) or CspZ-YA IgG samples (1 mg/kg, five mice per group). These CspZ-YA IgGs include total CspZ-YA IgG (total), those IgGs that recognize non-FH-binding site (non-FH-binding sites), or mouse monoclonal IgG no. 1139 or 1193. At 24 h after IgG inoculation, these mice were fed on by I. scapularis nymphs carrying B. burgdorferi B31-5A4 (Bb B31-5A4). An additional five mice inoculated with PBS but not fed on by ticks were included as the control (Uninfect.). The tissues were collected from those mice at 21dpf. Spirochete burdens at (B) the tick feeding site (bite site), (C) bladder, (D) ankles, and (E) heart were quantitatively measured at 21 dpf, shown as the number of spirochetes per 100 ng total DNA. Data shown are the geometric mean ± geometric standard deviation of the spirochete burdens from five mice per group. Statistical significances (P < 0.05, Kruskal-Wallis test with the two-stage step-up method of Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli) of differences in bacterial burdens relative to (*) uninfected mice or (#) between indicated groups of mice are presented.
