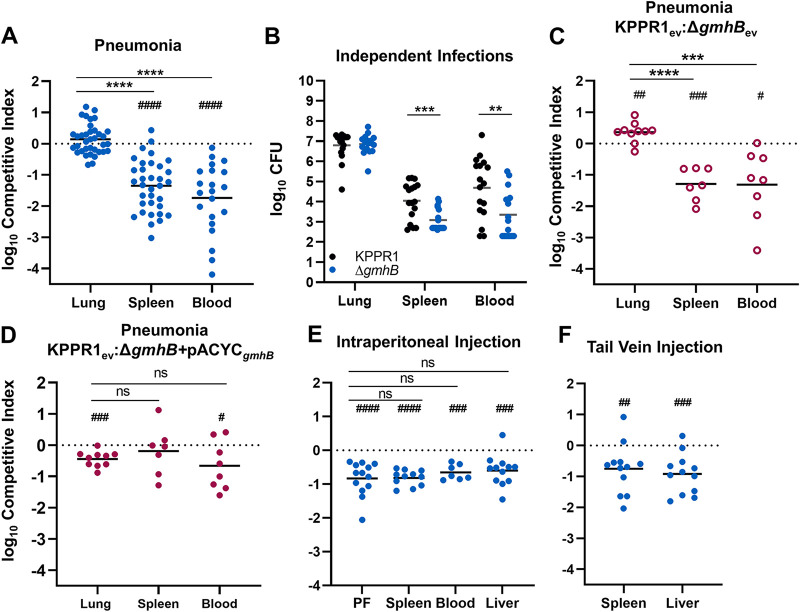
FIG 1.
GmhB enhances lung dissemination and bloodstream survival. In a model of bacteremic pneumonia, mice were retropharyngeally inoculated with 1 × 106 CFU K. pneumoniae (A to D). To initiate dissemination from a lung-independent site, 1 × 103 CFU was administered to the intraperitoneal cavity (E). For modeling direct bacteremia requiring no dissemination, 1 × 105 CFU was administered via tail vein injection (F). The 1:1 inoculum consisted of KPPR1:ΔgmhB (A, E, F), KPPR1:ΔgmhB carrying empty pACYC vector (ev; C), or KPPR1ev:ΔgmhB with gmhB complementation provided on pACYC under the control of the native gmhB promoter (ΔgmhB+pACYCgmhB; D). Independent infections used either KPPR1 or ΔgmhB alone at a 1 × 106 CFU dose (B). Mean log10 competitive index or CFU burden at 24-h postinfection is displayed. **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001 by unpaired t test; ##, P < 0.01; ###, P < 0.001; ####, P < 0.0001 by one sample t test with a hypothetical value of zero. For each group, n ≥ 7 mice in at least two independent infections. PF, peritoneal fluid.