FIGURE 5.
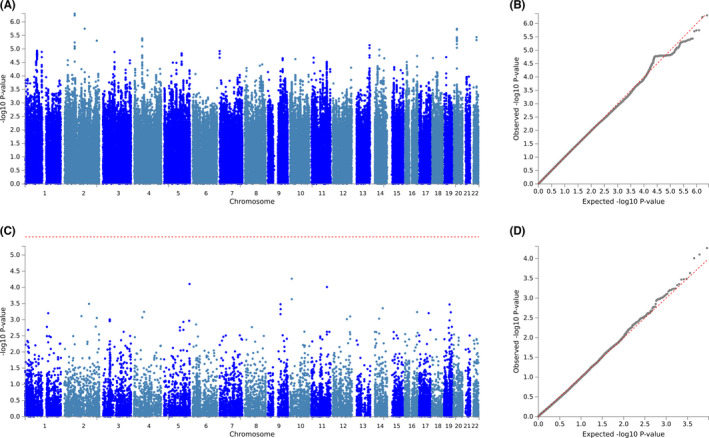
Genome‐wide single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) and gene‐based association studies of cisplatin‐induced peripheral sensory neuropathy (A) Manhattan plot of genome‐wide association study (GWAS) results for cisplatin‐induced peripheral sensory neuropathy. (B) Quantile–Quantile plot of GWAS results for cisplatin‐induced peripheral sensory neuropathy. Covariates in both GWAS include age at diagnosis and 10 European genetic principal components accounting for population substructure. (C) Manhattan plot of the gene‐based association analysis identifies no genome‐wide significant genes. Summary statistics for SNP‐based GWAS were uploaded to functional mapping and annotation to run a gene‐based association analysis based on a multiple linear principal components regression to determine the aggregated effect of all SNPs within a gene. Inputted SNPs were mapped to 18,106 protein coding genes, producing a significance threshold of p = 0.05/18,106 (2.8 × 10−6). (D) Quantile–Quantile plot of results from the gene‐based association analysis
