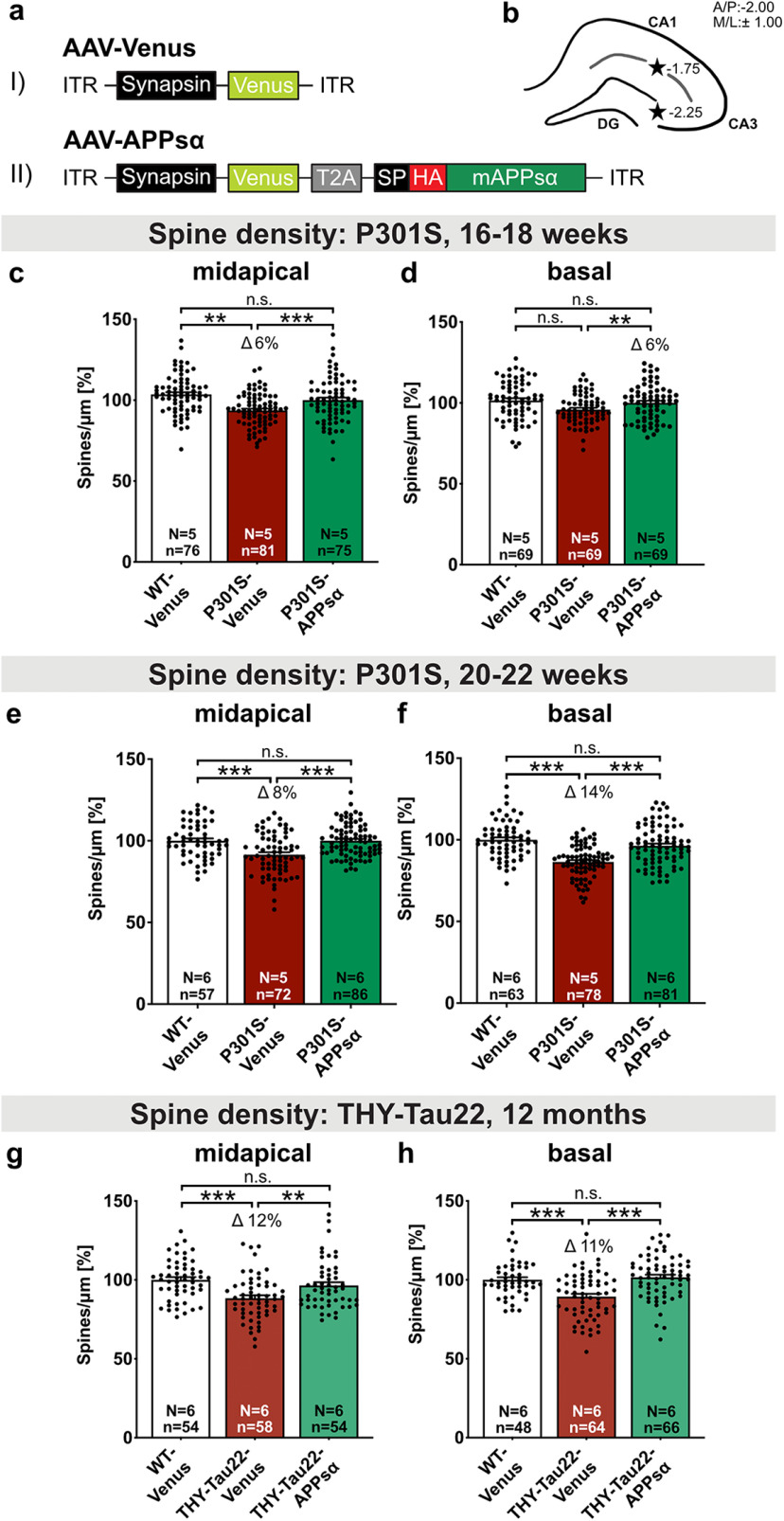
Figure 7.
AAV-APPsα expression rescues spine density deficits in P301S and THY-Tau22 mice. a, Schematic representation of monocistronic and bicistronic AAV constructs enabling neuron-specific expression of (aI) Venus and (aII) HA-tagged APPsα linked via a T2A side with Venus. ITR, Inverted terminal repeat; Synapsin, neuron-specific promotor; T2A, Thosea asigna virus 2A site; SP, signal peptide; HA, influenza hemagglutinin tag used to visualize APPsα. b, Scheme of the hippocampus with coordinates of the two injection sites for intracranial AAV injection (black stars). c, d, The spine density deficit of Venus-injected P301S mice is rescued by APPsα to WT control levels at 16-18 weeks of age. c, Spine density in midapical CA1 dendrites was reduced by 6% in P301S-Venus mice compared with the WT-Venus group (**p = 0.0029) and rescued by the injection of AAV-APPsα (WT-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: not significant; P301S-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: Δ 10%, ***p < 0.0001). d, The spine density of basal CA1 dendrites was comparable in WT and P301S mice. APPsα led to a significant increase in basal spine density in P301S-APPsα-injected mice compared with P301S-Venus injected mice (WT-Venus vs P301S-Venus: not significant; P301S-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: Δ 6%, **p = 0.0078; WT-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: not significant). e, f, The spine density deficit of Venus-injected P301S mice is rescued by APPsα to WT control levels at 20-22 weeks of age. e, The spine density deficit in midapical CA1 dendrites of P301S-Venus mice amounted to ∼8% and was rescued to WT levels by the injection of AAV-APPsα (WT-Venus vs P301S-Venus: ***p < 0.0001, WT-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: not significant; P301S-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: Δ 8%, ***p < 0.0001). f, In basal CA1 dendrites, the spine density deficit of Venus-injected P301S mice was normalized to WT level by the expression of APPsα (WT-Venus vs P301S-Venus: Δ 14%, ***p < 0.0001, WT-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: not significant; P301S-Venus vs P301S-APPsα: Δ 11% ***p < 0.0001). g, h, The spine density deficit of Venus-injected THY-Tau22 mice is rescued by APPsα to WT control levels at 12 months of age. g, Spine density in midapical CA1 dendrites was reduced by 12% in THY-Tau22-Venus mice compared with the WT-Venus group (***p < 0.0001) and rescued by the injection of AAV-APPsα (WT-Venus vs THY-Tau22-APPsα: not significant; THY-Tau22-Venus vs THY-Tau22-APPsα: Δ 8%, **p = 0.0077). h, In basal CA1 dendrites, the spine density deficit of Venus-injected THY-Tau22 mice was normalized to WT level by the expression of APPsα (WT-Venus vs THY-Tau22-Venus: Δ 11%, ***p = 0.0001, WT-Venus vs THY-Tau22-APPsα: not significant; THY-Tau22-Venus vs THY-Tau22-APPsα: Δ 12% ***p < 0.0001). Data are mean ± SEM. n = number of analyzed segments; N = number of animals per condition. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.