Figure 1: Mechanisms of ET-1 signaling in OPCs.
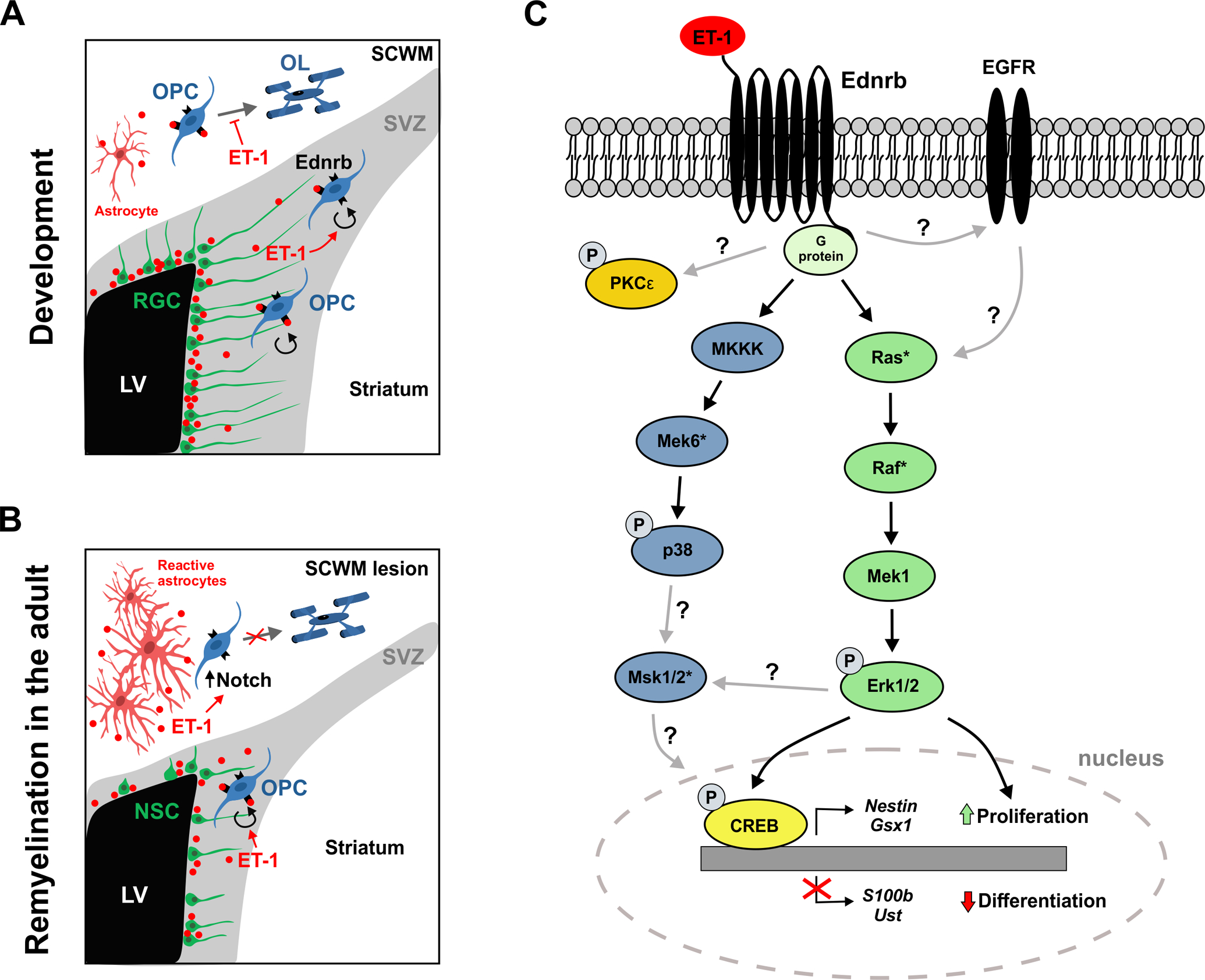
(A) Schematic describing inter-cellular ET-1 signaling in the early postnatal mouse subventricular zone (SVZ) and subcortical white matter (SCWM). Radial glial cells (RGC) in the SVZ secrete ET-1 which binds to Ednrb receptors on OPCs to promote their proliferation. Astrocytes in the SCWM secrete ET-1 which binds to Ednrb receptors on OPCs to block their differentiation. LV = lateral ventricle. (B) Schematic describing inter-cellular ET-1 signaling in the adult mouse following focal demyelination of the SCWM. Neural stem cells (NSCs) in the SVZ upregulate ET-1 which binds to Ednrb receptors on OPCs to promote their proliferation. Reactive astrocytes in the SCWM lesion secrete high levels of ET-1, which indirectly activates Notch signaling in OPCs and blocks their differentiation. LV = lateral ventricle. (C) Proposed intracellular signaling pathways activated by ET-1 signaling in OPCs. ET-1 binding to the Ednrb receptor primarily activates the MAPK/Erk pathway, leading to CREB phosphorylation and transcriptional changes that promote proliferation and progenitor maintenance. Black arrows indicate well-established protein interactions in OPCs, while gray arrows indicate protein interactions that have been described in other cell types, but remain uncharacterized in OPCs. Asterisks denote proteins that still require confirmation of activation upon ET-1 signaling in OPCs.
