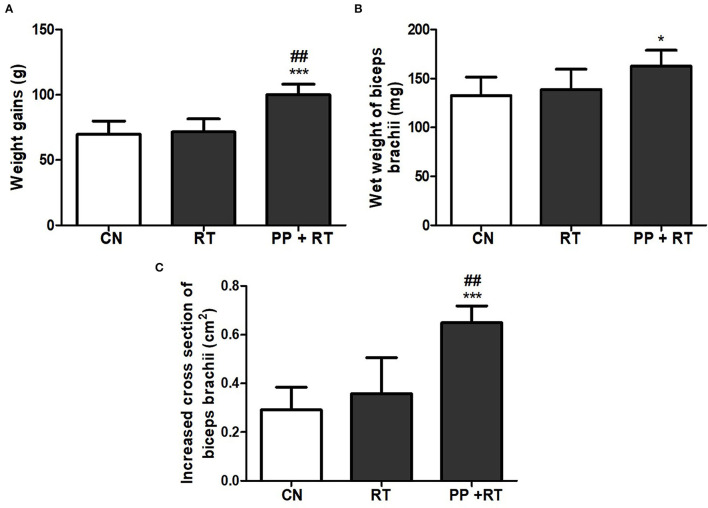
Figure 1.
Pea peptide supplementation combined with resistance exercise induced elevated muscle thickness and weight gains. (A) Body weight gains of the rats in CN, RT, and PP+RT group. (B) Wet weight of biceps brachii in the rats of CN, RT, and PP+RT group. (C) Increased cross-section of biceps brachii in the rats of CN, RT, and PP+RT group. CN: Control group, the rats were intragastrically administered with same volume of saline; RT: Resistance training group, the rats were carried out 3 times each week of resistance exercise training; PP+RT: Pea peptide supplementation combined with resistance exercise training group, the rats were daily intragastrically administered with 0.4 g/kg body weight of pea peptides and performed three times each week of resistance exercise training. The significant difference between groups was validated with one-way ANOVA using GraphPad Prism 6, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.01 vs. CN group, and ##p < 0.01 vs. RT group (n = 5/group). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (M ± SD).