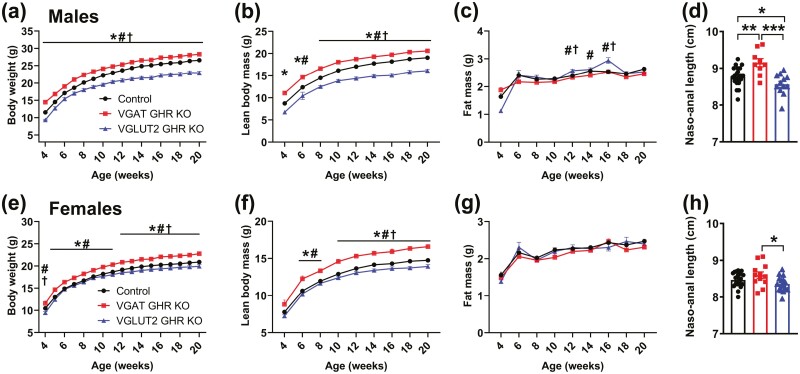
Figure 5.
Opposite effects on body growth of GHR ablation in GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons. A to C, Changes along time in body weight, lean body mass, and body fat mass in male control (n = 41), VGAT GHR KO (n = 41), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 15) mice. *P < .05, VGAT GHR KO vs control. #P < .05, VGAT GHR KO vs VGLUT2 GHR KO. † P < .05, VGLUT2 GHR KO vs control (repeated-measures 2-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons test). D, Naso-anal length of male control (n = 22), VGAT GHR KO (n = 9), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 12) mice. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .001 (1-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons test). E to G, Changes along time in body weight, lean body mass, and body fat mass in female control (n = 43), VGAT GHR KO (n = 15), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 15) mice. H, Naso-anal length of female control (n = 23), VGAT GHR KO (n = 12), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 16) mice. ANOVA, analysis of variance; GHR, growth hormone receptor; KO, knockout; VGAT, vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter.