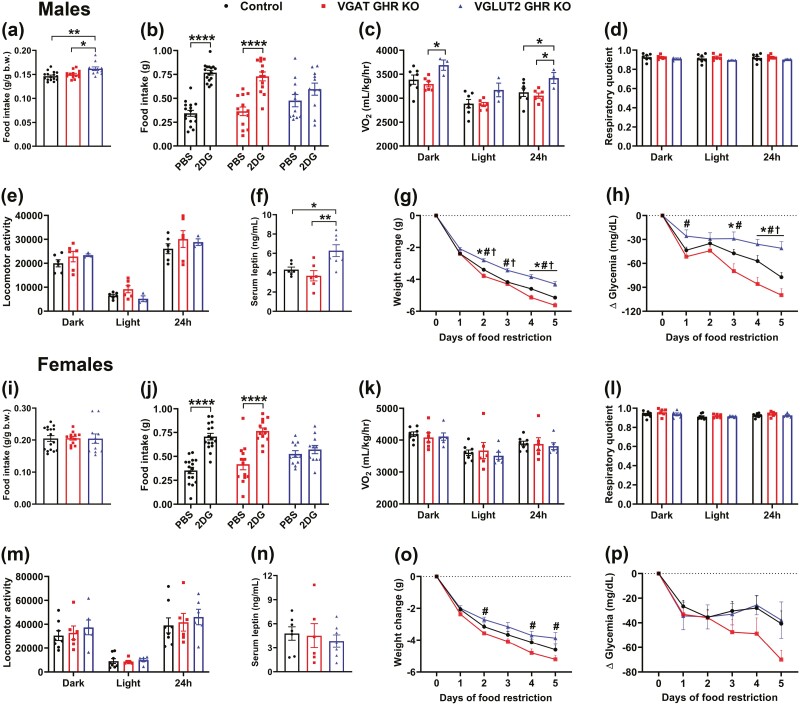
Figure 8.
GHR ablation in VGAT- and VGLUT2-expressing cells leads to different metabolic changes. A, Food intake relative to body weight in approximately 20-week-old control (n = 16), VGAT GHR KO (n = 13), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 11) male mice. *P < .05; **P < .01 (1-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons test). B, 2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2DG)-induced feeding response in control (n = 16), VGAT GHR KO (n = 13), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 11) male mice. ****P < .0001 (repeated-measures 2-way ANOVA and Bonferroni multiple comparisons test). C to E, VO2, respiratory quotient and locomotor activity in control (n = 7), VGAT GHR KO (n = 6), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 3) male mice. F, Serum leptin levels in control (n = 6), VGAT GHR KO (n = 6), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 7) male mice. *P < .05; **P < .01 (1-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons test). G and H, Changes in body weight and blood glucose levels during 5 days of 60% food restriction in control (n = 16), VGAT GHR KO (n = 13), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 11) male mice. *P < .05, VGAT GHR KO vs control. #P < .05, VGAT GHR KO vs VGLUT2 GHR KO. †P < .05, VGLUT2 GHR KO vs control (repeated-measures 2-way ANOVA and Newman-Keuls multiple comparisons test). I, Food intake relative to body weight in approximately 20-week-old control (n = 16), VGAT GHR KO (n = 12), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 11) female mice. J, 2DG-induced feeding response in control (n = 16), VGAT GHR KO (n = 13), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 11) female mice. K to M, VO2, respiratory quotient, and locomotor activity in control (n = 6), VGAT GHR KO (n = 6), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 6) female mice. N, Serum leptin levels in control (n = 7), VGAT GHR KO (n = 6), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 7) female mice. O and P, Changes in body weight and blood glucose levels during 5 days of 60% food restriction in control (n = 8), VGAT GHR KO (n = 7), and VGLUT2 GHR KO (n = 5) female mice. ANOVA, analysis of variance; GH, growth hormone; GHR, GH receptor; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; mRNA, messenger RNA; KO, knockout; VGAT, vesicular inhibitory amino acid transporter; VO2, oxygen consumption.