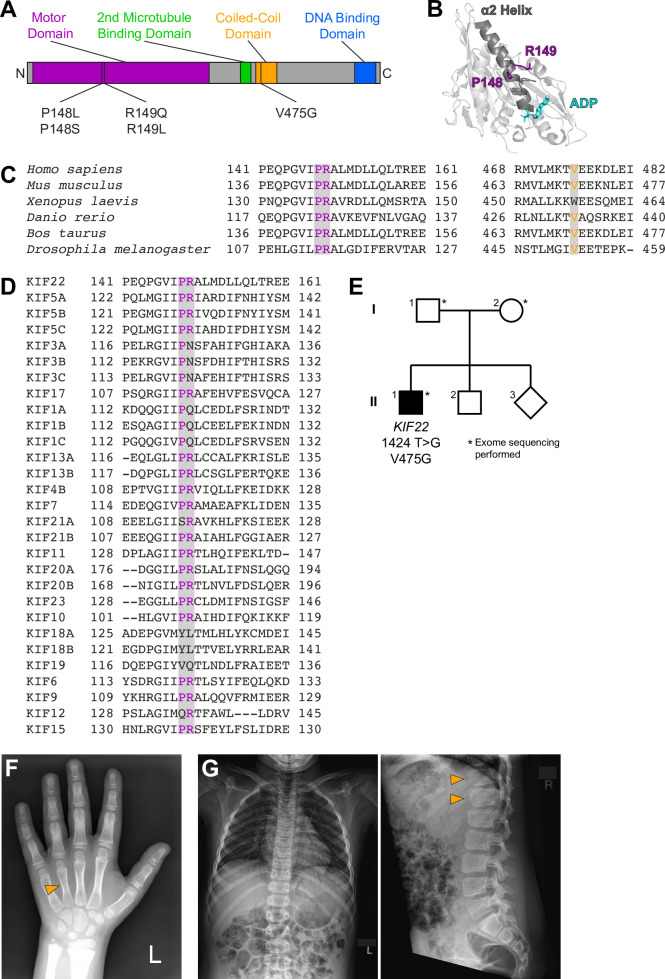
Figure 1. Identification of a novel pathogenic mutation in the tail of KIF22.
(A) Schematic of the domains of KIF22 with pathogenic mutations in the motor domain (magenta) and coiled-coil domain (yellow) indicated. (B) Location of amino acids P148 and R149 in the α2 helix of the KIF22 motor domain (PDB 6NJE). (C) Alignment of amino acid sequences of kinesin-10 family members to assess conservation of motor domain (P148 and R149, left) and coiled-coil domain (V475G, right) residues across species. (D) Alignment of amino acid sequences of human kinesin motors to assess conservation of motor domain residues across the kinesin superfamily. For (C, D), alignments were performed using Clustal Omega. (E) Pedigree identifying the de novo V475G (1424T>G) mutation. (F) Radiograph of the patient’s hand, posteroanterior view. Arrowhead indicates mild foreshortening of the fourth metacarpal. (G) Radiographs of the patient’s spine. Left: anteroposterior view, right: lateral view. Arrowheads indicate ‘bullet-shaped’ lower thoracic vertebrae.