Figure 5. DecoID increases the identification rate in a human plasma DIA dataset.
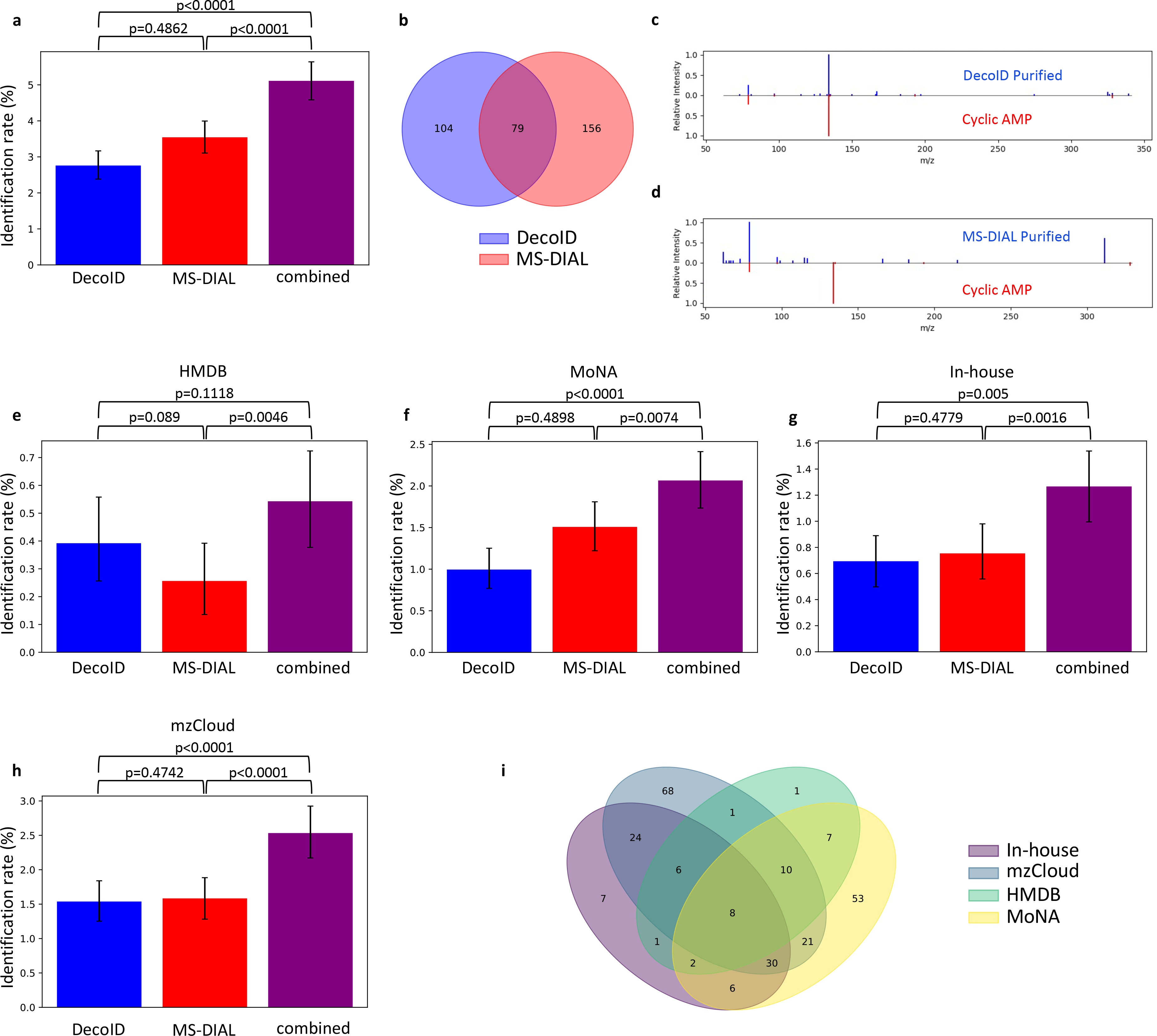
DecoID and MS-DIAL were applied to a plasma DIA dataset. All features detected by MS-DIAL were deconvolved with both DecoID and MS-DIAL. The deconvolved spectra were searched against HMDB, MoNA, the in-house database, and mzCloud. The results from MS-DIAL and DecoID were combined by taking the best hit for each feature amongst the results from MS-DIAL and DecoID (combined). (a) when combining the results for all databases, this parallel approach yielded greater identification rates compared to using either method alone. (b) Venn diagram showing the overlap in features that are identified using either DecoID or MS-DIAL. (c-d) Example identification from the negative mode DIA dataset that was found after deconvolution with DecoID (c) but that would not have been possible when using MS-DIAL (d). Identification was confirmed with a retention time match. (e-h) Identification rates of DecoID, MS-DIAL, and the combined approach when applied to the plasma DIA dataset with HMDB (e), MoNA (f), our in-house database (g), and mzCloud (h). (i) Venn diagram showing which features were able to be identified from which database after combining the results of MS-DIAL and DecoID. Data shown in (a) and (e-h) represent mean identification rate +/− 95% empirical confidence interval derived from bootstrap resampling (n=10,000) the plasma DIA dataset and calculating the identification rate on each independently resampled dataset (Methods). Statistical significance in (a) and (e-h) was assessed through 1-sided comparison of the bootstrapped identification rate distributions (Methods).
