Figure 6. DecoID increases the identification rate of metabolites from a publicly available mouse xenograft RPLC/MS/MS dataset.
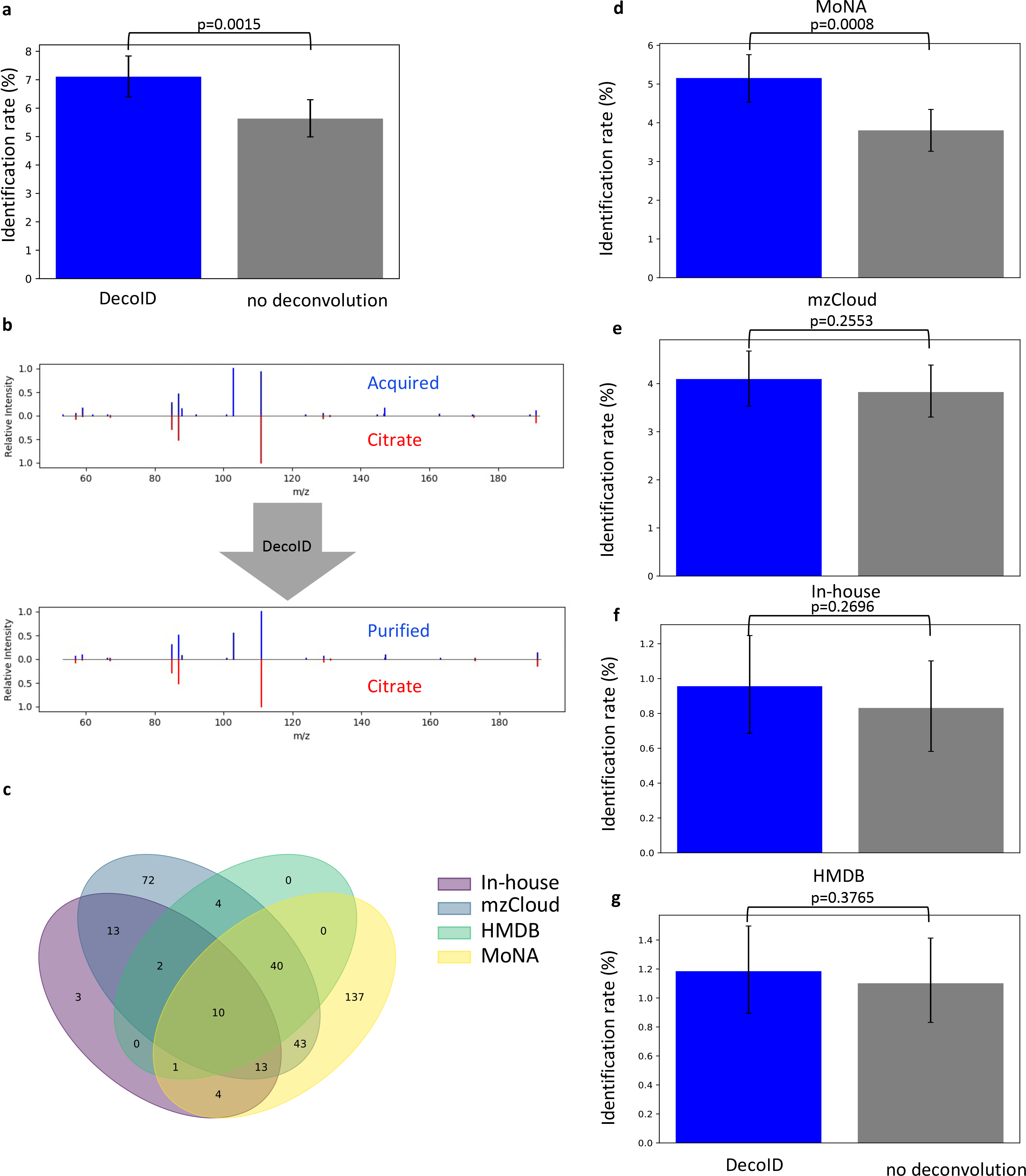
DecoID was applied to a published RPLC/MS/MS dataset31 uploaded to the MetaboLights repository. (a) DecoID increased the number of identifications made when aggregating the results from MoNA, mzCloud, the our in-house database, and HMDB. (b) Example deconvolution from the mzCloud database that led to the identification of citrate (bottom) that was not possible without deconvolution (top). (c) Using multiple databases provide complementary identifications. The Venn diagram shows which features were able to be identified from which databases after deconvolution. (d-g) Identification rates when using DecoID and no deconvolution to identify metabolites in the RPLC/MS/MS dataset with MoNA (d), mzCloud (e), in-house databse (f), and HMDB (g). With all databases, DecoID increased the identification rate compared to no deconvolution. Data shown in (a) and (d-g) represent the mean identification rate +/− 95% empirical confidence interval derived from bootstrap resampling (n=10,000) the RPLC/MS/MS dataset and calculating the identification rate on each independently resampled dataset (Methods). Statistical significance in (a) and (d-g) was assessed through 1-sided comparison of the bootstrapped identification rate distributions (Methods).
