FIGURE 2.
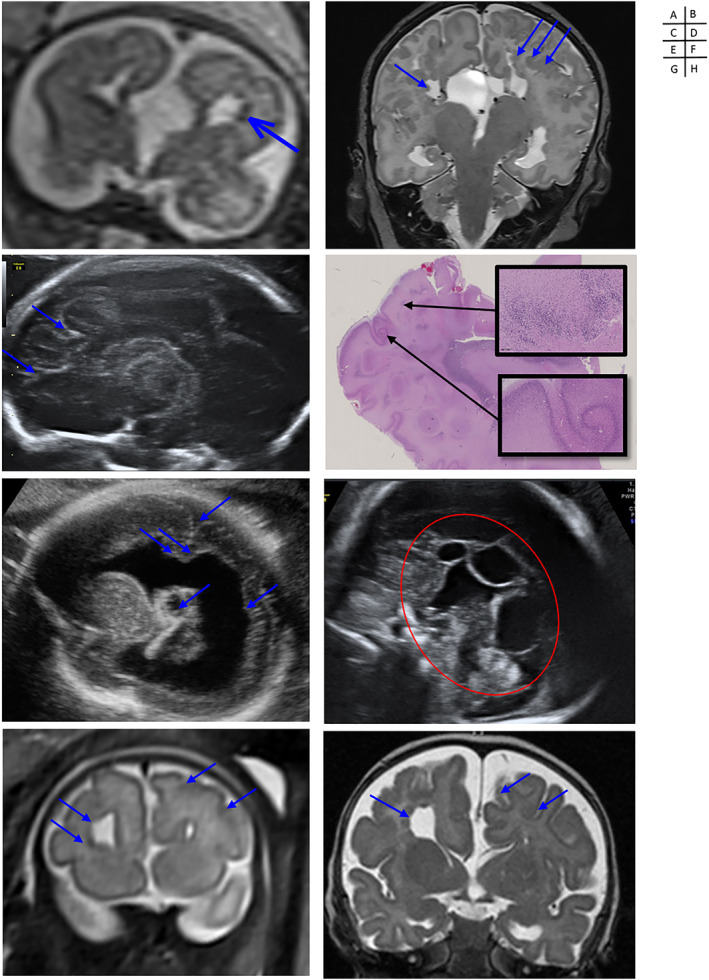
Prenatal/postnatal imaging and pathological aspect of cortical abnormalities associated with Aicardi Syndrome. Case 2: (A) Prenatal (T2w, coronal, 25w) and (B) postnatal MRI (T2w, coronal) showing complete agenesis of the corpus callosum, with interhemispheric cysts, distorsion of the interhemispheric fissure, and subependymal, periventricular and cortico‐subcortical heterotopias (courtesy of Yvan Vial and Sébastien Lebon). Case 3: (C) US (parasagittal section at 22w) and (D) giant and X10 histo‐pathological sections (hematoxylin and eosin stain) of the left parietal lobe showing an association of polymicrogyria and heterotopias (courtesy of Léo Pomar and Estelle Dubruc). Case 12: (E) US (parasagittal, 24w) showing severe unilateral ventriculomegaly with periventricular heterotopias, choroid plexus cyst and polymicrogyria(courtesy of José Ochoa). Case 13: (F) US (medio‐sagittal section at 31w) showing a complete agenesis of the corpus callosum associated with juxtaposed interhemispheric cysts (courtesy of José Ochoa). Case 16: (G) Prenatal (T2w, coronal, 33w) and (H) postnatal MRI (T2w, coronal) showing complete agenesis of the corpus callosum associated with a distorsion of the interhemispheric fissure, polymicrogyria (on the side of the enlarged frontal horn) and periventricular heterotopias (arrows) (courtesy of Thierry A. G. M. Huisman)
