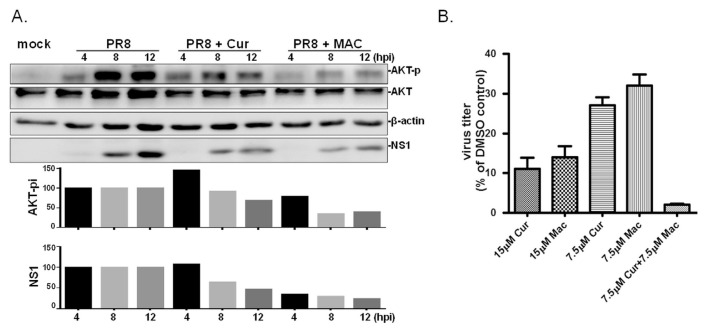
Fig. 4.
MAC dampens influenza virus-induced activation of AKT signalling pathway and works in synergy with Cur. (A) MDCK cells were treated with MAC or Cur at 1 h post IAV infection (at MOI of 5 viruses per cell); PR8 indicates cells infected with PR8 without treatment. The total proteins were harvested at 4, 8, 12 hpi. Basal level of AKT, the phosphorylated AKT (AKT-p), viral NS1 protein (NS1), and β-actin were simultaneously detected by Western blot analysis. This experiment was conducted twice and results presented with similar trends. The relative level of phosphorylated AKT and NS1 was normalized with basal AKT, or actin, respectively, in each sample. Subsequently, the relative level of AKT-p and NS1 in infected cells treated with MAC or Cur was estimated by comparing with those in mock treatment at the same time point. (B) MDCK cells were treated with MAC alone, or in combination with Cur at concentrations indicated at 8 h prior to IAV infection (2000 PFU). The tested compounds were present in the medium throughout the time of infection. The yield of viral progenies was determined at 24 hpi by standard plaque assay. The experiment was conducted three times and the relative viral titer was plotted as the percentage of plaque number to that of cells treated with DMSO, the solvent control.