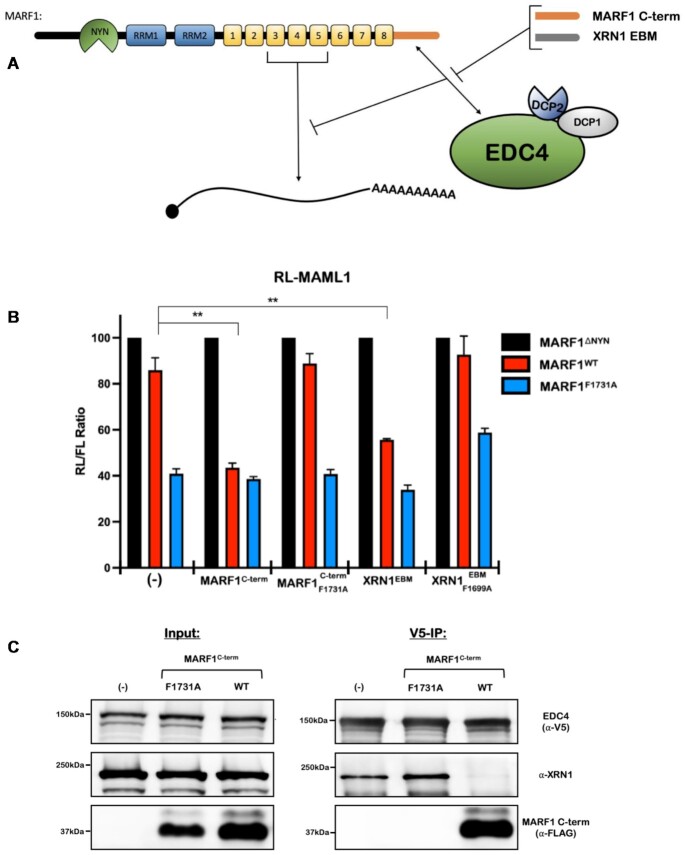
Figure 3.
MARF1 and XRN1 competitively interact with EDC4 in a mutually exclusive manner. (A) Schematic diagram representing the reporter assay in (B), where the MARF1C-term or the XRN1EBM compete with low levels of full-length MARF1 for interacting with endogenous EDC4. (B) RL-MAML1 activity detected in extracts of transfected HeLa cells expressing the annotated proteins and FL as a transfection normalization control. Histograms represent the mean RL activity detected from three biological replicates, normalized to FL activity and the RL/FL ratio of a catalytically inactive MARF1 (MARF1ΔNYN) set to 100. Error bars represent the SEM and statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed T-test comparing RL activity to the (-) samples for MARF1WT samples (**P < 0.01). (C) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments performed on HEK 293T cells stably expressing V5-tagged EDC4. Cells were transfected with MARF1 C-term variants and a puromycin selectable marker. Puromycin-selected cell lysates were subsequently incubated with V5-antibody and then analyzed by western blotting for the presence of endogenous XRN1.