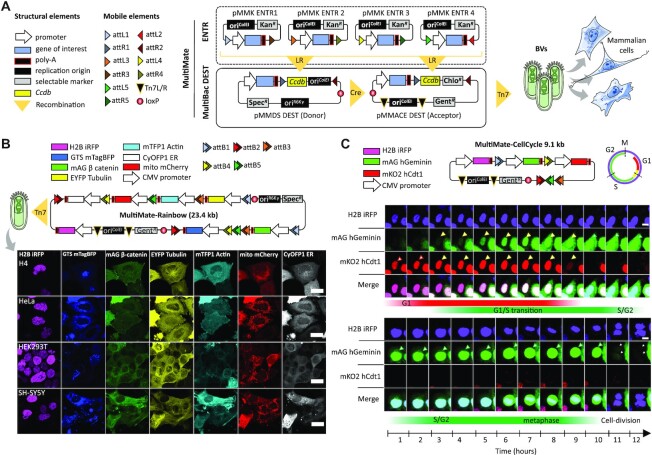
Figure 1.
MultiMate enables rapid modular assembly of multifunctional DNA circuitry for efficient baculovirus-vectored delivery in human cells. (A) MultiMate assembly platform in a schematic view. Symbols are listed (left panel). attL/R flanked DNA from ENTR plasmid modules (upper box, dashed) are assembled on MultiBac-DEST (lower box) and further combined by in vitro Cre-mediated recombination to generate multicomponent MultiMate plasmids, maximally eliminating prokaryotic backbone DNA sequences. MultiMate plasmids are integrated in BVs customized for efficient delivery in human cells (right panel). (B) Confocal live cell imaging of H4, HeLa, HEK293T and SH-SY5Y 48 hours after transduction with MultiMate-Rainbow BV (upper panel) evidencing in all cells homogeneous sustained expression and correct subcellular localization of H2B-iRFP (nucleus), GTS-mTagBFP (Golgi), mAG-β-catenin (membrane and adherens junctions), EYFP-Tubulin (microtubules), mTFP1-Actin (cytoskeleton), mito-mCherry (mitochondria) and CyOFP1-ER (endoplasmic reticulum). Scalebar, 20 μm. (C) Twelve-hours confocal time-lapse imaging of live HeLa cells transduced with MultiMate-CellCycle BV (snapshots, Supplementary Video 1). Transduced cells constitutively express H2B-iRFP for DNA imaging. mAG-hGeminin and mKO2-hCdt1 are stabilized in S/G2 and G1 cell cycle stages, respectively. Upper panel shows G1/S transition, lower panel shows a dividing cell (arrows indicate tracked cells). Scalebar, 10 μm. DNA elements, plasmid topology and cell cycle schematics are illustrated (upper panel).