FIGURE 1.
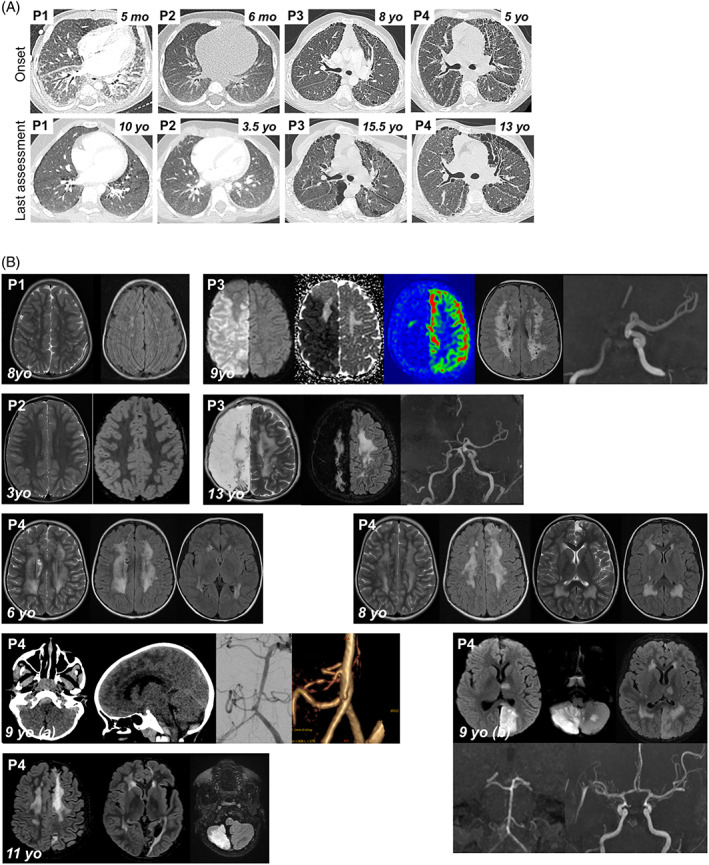
Clinical features of P1‐P4. (A) Pulmonary CT scan at disease onset and last assessment. P1: 5mo: Diffused ground glass opacities (GGO) with antero‐posterior density gradient and presence of sub‐pleural posterior consolidations. Thickening of interlobular septa in the lower lobes and of fissures; 10yo: Low‐density GGO, microcysts with subpleural distribution and along interlobular septa. P2: 6mo: normal; 3.5yo: Subpleural thickened interlobular septa in middle lobe. P3: 8yo: Mild pattern of fibrosing interstitial lung disease (ILD) with thickening, few cysts and no honeycombing; 15.5yo: confluence in large macrocysts. Pectus carinatum. P4: 5yo: Fibrosing ILD with thickening of intralobular lines, interlobular septa and fissures. Numerous subpleural microcysts with honeycombing especially in the left lung; 13yo: Fibrosis worsening with increase in size and number of cysts. Lung volumes are preserved despite worsening of thoracic deformation (pectus carinatum). (B) Brain MRIs. P1, 8yo: Bilateral punctiform subcortical and deep white matter hyperintensities on T2 weighted images (T2WI) and fluid‐attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) suggesting vascular leukoencephalopathy. P2, 3yo: Normal T2WI and FLAIR MRI. P3, 9yo: Acute right ischemic stroke: diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) hypersignal, decreased apparent diffusion coefficient, and decreased cerebral blood flow in arterial spin labelling in the middle and anterior cerebral artery territories. Time‐of‐flight MR angiogram showing occlusion of the terminal right internal carotid artery; bilateral diffuse subcortical and deep white matter hyperintensities on FLAIR images (chronic leukoencephalopathy). P3, 13yo: Leukoencephalomalacia resulting from extensive right hemisphere infarction, worsening of white matter changes on T2WI and FLAIR images. P4, 6yo: Bilateral diffuse deep white matter hyperintensities, with cavitation on T2WI and FLAIR images (chronic leukoencephalopathy). P4, 8yo: worsening of chronic leukoencephalopathy, and left frontal cortical atrophy, on T2WI and FLAIR images, suggestive of clinically asymptomatic ischemic injury. P4, 9yo: (A) Brain CT scan: Posterior fossa subarachnoid haemorrhage with ruptured aneurysm located on the right posterior inferior cerebellar artery. (B) 7 days later, acute stroke in vertebro‐basilar territory, including left cerebral posterior territory in DWI, secondary to diffuse vasospasm on Time‐of‐flight MR angiogram. P4, 11yo: Cortical and sub‐cortical ischemic sequelae of previous strokes within multiple arterial territories (left anterior cerebral artery, left posterior cerebral artery, cerebellum), worsening of diffuse white matter changes [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
