Figure 1.
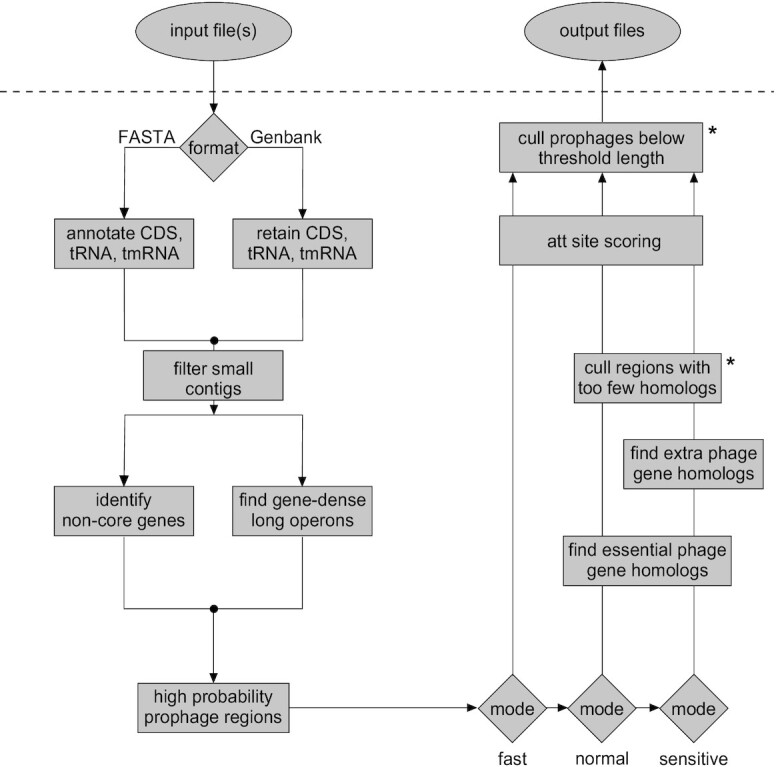
Workflow for DEPhT. Input files may be in either FASTA or Genbank flat file format. For FASTA files, contigs are parsed and CDS, tRNA and tmRNA genes are annotated. For Genbank files, contigs are parsed and annotations are reduced to CDS, tRNA and tmRNA genes. Annotated CDS genes are examined for (i) global homology to conserved mycobacterial genes and (ii) size, spacing, and transcription directionality change frequency. Genomic islands with gene architecture similar to that seen in temperate phages are identified as high likelihood prophage regions. In normal or sensitive run modes, the CDS genes in these regions are searched against a database of HMMs of genes performing phage-specific functions such as integrase, lysin, capsid, and terminase. In sensitive run mode genes are searched against a larger HMM database that includes any additional functionally annotated gene families. The sensitive mode thus yields a reasonably complete prophage sequence annotation. These limited homology searches help to distinguish true intact prophages from false positive prophage-like regions. Remaining prophage regions are searched for the phage attachment sites (attL/attR) before output files are generated. Asterisks indicate components that use thresholds that may be adjusted by users.
