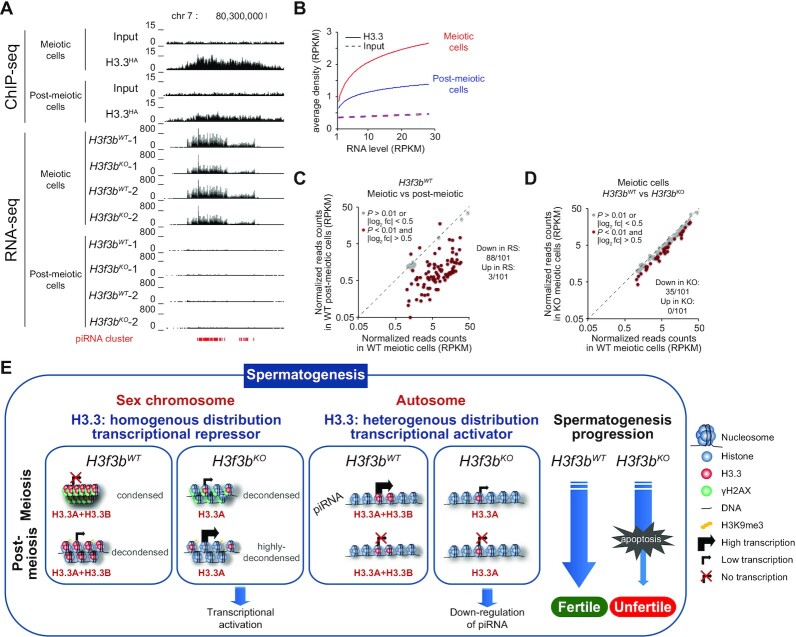
Figure 6.
H3.3 regulates the expression of piRNA in meiotic cells. (A) Upper part. Double immunoaffinity purification of the HA-FLAG-tagged H3.3 mononucleosomes, followed by massive sequencing of ‘immunopurified’ nucleosomal DNA (ChIP-seq) were carried out to determine the genome-wide localization of H3.3. Example of strong H3.3 enrichment on piRNA cluster located on chromosome 7 in both meiotic and post-meiotic cells; lower part, expression profiles (RNA-seq) of the indicated piRNA cluster (indicated in red) from chromosome 7 in H3f3bWT and H3f3bKO meiotic and post-meiotic cells. In both cases two biologically independent experiments were presented. (B) The genome-wide expression level of piRNA clusters positively correlates with the amount of associated H3.3 in both meiotic and post-meiotic cells. (C) The meiotic/post-meiotic transition is associated with a ∼10-fold decrease in piRNA expression. (D) The absence of H3.3B is accompanied with a decrease of ∼25% of the expression of the piRNA clusters in meiotic cells. (E) Schematics depicting the dual role of H3.3 in spermatogenesis.