Figure 3.
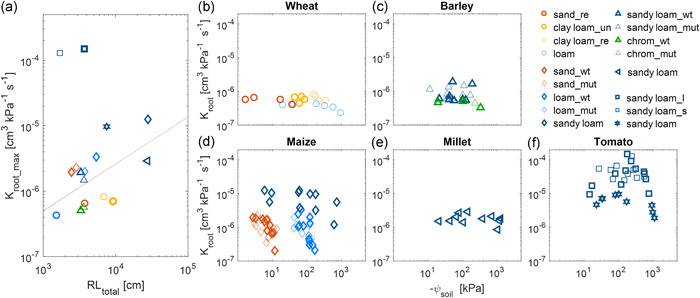
Variation of root hydraulic conductance (K root) of different species in drying soils. (a) Relation between root hydraulic conductance (K root_max) in wet conditions and measured total root length (RL total). The regression line excluded the grafted tomatoes (square) (r 2 = 0.35, p = 0.027). (b–f) Variation of K root in drying soils. In subplot (d), maize in sandy loam (dark cyan diamond) was around 2 weeks older than maize in sand and loam. In subplot (f), tomatoes with long (thick square) and short (thin square) root systems were grafted with an identical shoot whereas the one with hexagon symbol was not grafted. The grafted tomatoes were around 10 days older than the nongrafted ones. Millet (e) and tomato (f) were grown in the same sandy loam soil. The difference in plants and soils is shown in Table 1 and Figure 2. chrom, red chromosol soil; l, long root system; mut, mutant; re, repacked; s, short root system; un, undisturbed; wt, wild type. The same colour is used for similar soil textures [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
